Endothelial podosome rosettes regulate vascular branching in tumour angiogenesis
- PMID: 25218639
- PMCID: PMC4564017
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3036
Endothelial podosome rosettes regulate vascular branching in tumour angiogenesis
Abstract
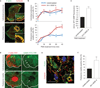
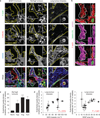
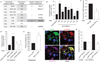
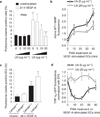
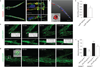
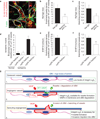
The mechanism by which angiogenic endothelial cells break the physical barrier of the vascular basement membrane and consequently sprout to form new vessels in mature tissues is unclear. Here, we show that the angiogenic endothelium is characterized by the presence of functional podosome rosettes. These extracellular-matrix-degrading and adhesive structures are precursors of de novo branching points and represent a key feature in the formation of new blood vessels. VEGF-A stimulation induces the formation of endothelial podosome rosettes by upregulating integrin α6β1. In contrast, the binding of α6β1 integrin to the laminin of the vascular basement membrane impairs the formation of podosome rosettes by restricting α6β1 integrin to focal adhesions and hampering its translocation to podosomes. Using an ex vivo sprouting angiogenesis assay, transgenic and knockout mouse models and human tumour sample analysis, we provide evidence that endothelial podosome rosettes control blood vessel branching and are critical regulators of pathological angiogenesis.
Figures

Comment in
-
Angiogenesis: pushing through, branching out.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Nov;14(11):704-5. doi: 10.1038/nrc3841. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25291293 No abstract available.
-
Cell adhesion: Winning mechanism for angiogenesis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Nov;15(11):702. doi: 10.1038/nrm3893. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25315274 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hallmann R, et al. Expression and function of laminins in the embryonic and mature vasculature. Physiol. Rev. 2005;85:979–1000. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med. 2003;9:669–676. - PubMed
-
- Inoue M, Hager JH, Ferrara N, Gerber HP, Hanahan D. VEGF-A has a critical, nonredundant role in angiogenic switching and pancreatic beta cell carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:193–202. - PubMed
-
- Galvez BG, Matias-Roman S, Albar JP, Sanchez-Madrid F, Arroyo AG. Membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase is activated during migration of human endothelial cells and modulates endothelial motility and matrix remodeling. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:37491–37500. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

