miR-22 in cardiac remodeling and disease
- PMID: 25218673
- PMCID: PMC4171194
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2014.07.005
miR-22 in cardiac remodeling and disease
Abstract
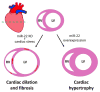
Regulation of gene expression during cardiac development and remodeling is very complicated, involving epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and translational regulation. Our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying cardiac remodeling is still far from complete. MicroRNAs are a class of small non-coding RNAs that have been shown to play critical roles in gene regulation in cardiovascular biology and disease. microRNA-22 (miR-22) is an evolutionally conserved miRNA that is highly expressed in the heart. Recent studies uncovered miR-22 as an important regulator for cardiac remodeling. miR-22 modulates the expression and function of genes involved in hypertrophic response, sarcomere reorganization, and metabolic program shift during cardiac remodeling. In this review, we will focus on the recent findings of miR-22 in cardiac remodeling and the therapeutic potential of this miRNA in the treatment of related defects resulting from adverse cardiac remodeling.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Hill JA, Olson EN. Cardiac plasticity. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1370–1380. - PubMed
-
- Lagos-Quintana M, et al. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science. 2001;294:853–858. - PubMed
-
- Lau NC, et al. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:858–862. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Ambros V. An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:862–864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

