Quadriceps/hamstrings co-activation increases early after total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 25218971
- PMCID: PMC5433797
- DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2014.08.001
Quadriceps/hamstrings co-activation increases early after total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
Quadriceps and hamstrings weakness and co-activation are present following total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and may impair functional performance. How surgery and post-operative rehabilitation influence muscle activation during walking early after surgery is unclear.
Purpose: Examine muscle strength and activation during walking before and one and 6-months post-TKA.
Methods: Ten patients (n=6 female; age: 64.7 ± 7.9 years; body mass index[BMI]:29.2 ± 2.5 kg/m(2)) and 10 healthy adults (n=6 female; age: 60.6 ± 7.4 years; BMI: 25.5 ± 4.0 kg/m(2)) participated. The patients underwent bilateral quadriceps and hamstrings strength testing and assessment of quadriceps/hamstrings co-activation and on/off timing using surface electromyography during a six-minute walk test (6MW). Groups, limbs, and changes with TKA surgery were compared.
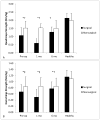
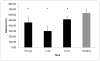
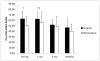
Results: Patients reported greater 6MW knee pain pre- versus post-TKA and compared to controls (P<0.05). Patients had weaker surgical limb hamstrings (P<0.05) and bilateral quadriceps (P<0.05) strength than controls pre- and post-TKA. Before and 1-month post-TKA, patients had side-to-side differences in quadriceps and hamstrings strength (P<0.05). Controls walked farther than patients (P<0.01). Patients demonstrated greater surgical limb co-activation pre-operatively than controls (P<0.05). Co-activation was higher bilaterally one-month post-TKA compared to controls (P<0.05). Patients turned off their quadriceps later during stance than controls before and 1-month post-TKA (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Muscle strength, co-activation, and timing differed between patients and controls before and early after surgery. Rehabilitation to improve strength and muscle activation seems imperative to restore proper muscle firing patterns early after surgery.
Keywords: Muscle activity; Strength; Total knee replacement; Walking.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Loughead JM, Malhan K, Mitchell SY, et al. Outcome following knee arthroplasty beyond 15 years. Knee. 2008 Mar;15(2):85–90. - PubMed
-
- Noble PC, Gordon MJ, Weiss JM, Reddix RN, Conditt MA, Mathis KB. Does total knee replacement restore normal knee function? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005 Feb;(431):157–165. - PubMed
-
- Huang CH, Cheng CK, Lee YT, Lee KS. Muscle strength after successful total knee replacement: a 6- to 13-year followup. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996 Jul;(328):147–154. - PubMed
-
- Silva M, Shepherd EF, Jackson WO, Pratt JA, McClung CD, Schmalzried TP. Knee strength after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003 Aug;18(5):605–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

