Circulating tumor cell telomerase activity as a prognostic marker for overall survival in SWOG 0421: a phase III metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer trial
- PMID: 25219358
- PMCID: PMC4323674
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.29212
Circulating tumor cell telomerase activity as a prognostic marker for overall survival in SWOG 0421: a phase III metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer trial
Abstract
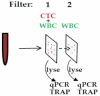
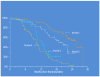
Circulating tumor cells (CTC) are promising biomarkers in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), and telomerase activity (TA) is a recognized cancer marker. Therefore, we hypothesized that CTC TA may be prognostic of overall survival (OS) in mCRPC. To test this, we used a novel Parylene-C slot microfilter to measure live CTC TA in S0421, a phase III SWOG-led therapeutic trial. Blood samples underwent CTC capture and TA measurement by microfilter, as well as parallel enumeration by CellSearch (Janssen/J&J). Cox regression was used to assess baseline (pre-treatment) TA versus OS, and recursive partitioning was used to explore potential prognostic subgroups and to generate Kaplan-Meier (KM) OS curves. Samples were obtained from 263 patients and generated 215 TA measures. In patients with baseline CTC count ≥5 (47% of patients), higher CTC TA was associated with hazard ratio 1.14 (p = 0.001) for OS after adjusting for other clinical covariates including CTC counts and serum PSA at study entry. Recursive partitioning identified new candidate risk groups with KM OS curve separation based on CTC counts and TA. Notably, in men with an intermediate range baseline CTC count (6-54 CTCs/7.5 ml), low versus high CTC TA was associated with median survival of 19 versus 12 months, respectively (p = 0.009). Baseline telomerase activity from CTCs live-captured on a new slot microfilter is the first CTC-derived candidate biomarker prognostic of OS in a large patient subgroup in a prospective clinical trial. CTC telomerase activity thus merits further study and validation as a step towards molecular CTC-based precision cancer management.
Keywords: biomarker; circulating tumor cells; prognosis; prostate cancer; telomerase activity.
© 2014 UICC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combination of circulating tumor cell enumeration and tumor marker detection in predicting prognosis and treatment effect in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 8;6(39):41825-36. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6167. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26497689 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating tumor cell counts are prognostic of overall survival in SWOG S0421: a phase III trial of docetaxel with or without atrasentan for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2014 Apr 10;32(11):1136-42. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.51.7417. Epub 2014 Mar 10. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24616308 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Associations between AR-V7 status in circulating tumour cells, circulating tumour cell count and survival in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2019 Nov;121:48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.08.005. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Eur J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31542641
-
The use of circulating tumor cells in guiding treatment decisions for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.Cancer Treat Rev. 2016 May;46:42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016. PMID: 27107266 Review.
-
Clinical Utility of Circulating Tumor Cells in Advanced Prostate Cancer.Curr Oncol Rep. 2016 Jan;18(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s11912-015-0490-9. Curr Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26700506 Review.
Cited by
-
Telomere and Telomerase Therapeutics in Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2016 May 26;7(6):22. doi: 10.3390/genes7060022. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27240403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer transcriptomic profiling from rapidly enriched circulating tumor cells.Int J Cancer. 2020 May 15;146(10):2845-2854. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32915. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32037533 Free PMC article.
-
Improved detection of circulating tumor cells in non-metastatic high-risk prostate cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 21;6:39736. doi: 10.1038/srep39736. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 28000772 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of CTCs in portal vein was associated with intrahepatic metastases and prognosis in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer.J Cancer. 2018 May 22;9(11):2038-2045. doi: 10.7150/jca.23989. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29896289 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Tumor Cell Persistence Associates with Long-Term Clinical Outcome to a Therapeutic Cancer Vaccine in Prostate Cancer.J Pers Med. 2021 Jun 26;11(7):605. doi: 10.3390/jpm11070605. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34206815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Kelly WK, Halabi S, Carducci M George D, Mahoney JF, Stadler WM, Morris M, Kantoff P, Monk JP, Kaplan E, Vogelzang NJ, Small EJ. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial comparing docetaxel and prednisone with or without bevacizumab in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: CALGB 90401. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(13):1534–40. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fizazi KS, Higano CS, Nelson JB, Gleave M, Miller K, Morris T, Nathan FE, McIntosh S, Pemberton K, Moul JW. Phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of docetaxel in combination with zibotentan in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(14):1740–48. - PubMed
-
- Makarov DV, Loeb S, Getzenberg RG, Partin AW. Biomarkers for prostate cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 2009;60:139–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA012644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA22433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76448/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA63848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA37981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA093373/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA022433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA016385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA12644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA20319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063845/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA076447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA128567/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035192/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA014089-38/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA045807/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA128567/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA63845/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA141077/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA014028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035421/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA074647/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA11083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35421/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA063844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA31949/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA141077/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA016116/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35192/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA74647/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA020319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA042777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA42777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA011083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA21115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180819/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA31946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58723/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16116/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045807/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA068183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA045560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

