Iodine vapor staining for atomic number contrast in backscattered electron and X-ray imaging
- PMID: 25219801
- PMCID: PMC4285820
- DOI: 10.1002/jemt.22435
Iodine vapor staining for atomic number contrast in backscattered electron and X-ray imaging
Abstract
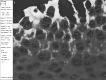
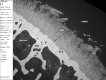
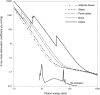
Iodine imparts strong contrast to objects imaged with electrons and X-rays due to its high atomic number (53), and is widely used in liquid form as a microscopic stain and clinical contrast agent. We have developed a simple technique which exploits elemental iodine's sublimation-deposition state-change equilibrium to vapor stain specimens with iodine gas. Specimens are enclosed in a gas-tight container along with a small mass of solid I2 . The bottle is left at ambient laboratory conditions while staining proceeds until empirically determined completion (typically days to weeks). We demonstrate the utility of iodine vapor staining by applying it to resin-embedded tissue blocks and whole locusts and imaging them with backscattered electron scanning electron microscopy (BSE SEM) or X-ray microtomography (XMT). Contrast is comparable to that achieved with liquid staining but without the consequent tissue shrinkage, stain pooling, or uneven coverage artefacts associated with immersing the specimen in iodine solutions. Unmineralized tissue histology can be read in BSE SEM images with good discrimination between tissue components. Organs within the locust head are readily distinguished in XMT images with particularly useful contrast in the chitin exoskeleton, muscle and nerves. Here, we have used iodine vapor staining for two imaging modalities in frequent use in our laboratories and on the specimen types with which we work. It is likely to be equally convenient for a wide range of specimens, and for other modalities which generate contrast from electron- and photon-sample interactions, such as transmission electron microscopy and light microscopy.
Keywords: SEM; attenuation; desublimation; histology; microCT; segmentation; soft tissue.
© 2014 The Authors. Microscopy Research Technique published by Wiley Periodocals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quantitative analysis of microscopic X-ray computed tomography imaging: Japanese quail embryonic soft tissues with iodine staining.J Anat. 2013 Sep;223(3):297-310. doi: 10.1111/joa.12081. Epub 2013 Jul 22. J Anat. 2013. PMID: 23869493 Free PMC article.
-
Iodine-enhanced micro-CT imaging: methodological refinements for the study of the soft-tissue anatomy of post-embryonic vertebrates.J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2014 May;322(3):166-76. doi: 10.1002/jez.b.22561. Epub 2014 Jan 30. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2014. PMID: 24482316
-
Chemical effects of diceCT staining protocols on fluid-preserved avian specimens.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 18;15(9):e0238783. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238783. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32946473 Free PMC article.
-
Conventional and high resolution scanning electron microscopy of biological sectioned material.Scanning Microsc. 1991 Mar;5(1):135-44; discussion 144-5. Scanning Microsc. 1991. PMID: 2052919 Review.
-
Mouse embryo phenotyping using X-ray microCT.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 16;10:949184. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.949184. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36187491 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic characterization of wing mechanosensors that monitor airflow and wing deformations.iScience. 2022 Mar 22;25(4):104150. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104150. eCollection 2022 Apr 15. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35465360 Free PMC article.
-
On latches in biological systems: a comparative morphological and functional study of the retinaculum and the dens lock in Collembola.Front Zool. 2023 May 9;20(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12983-023-00491-2. Front Zool. 2023. PMID: 37161456 Free PMC article.
-
Scanning Electron Microscopy and Bone.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2885:621-670. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4306-8_31. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40448783
-
Tracheal branching in ants is area-decreasing, violating a central assumption of network transport models.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Apr 30;16(4):e1007853. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007853. eCollection 2020 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32352964 Free PMC article.
-
Iodine consumption and cognitive performance: Confirmation of adequate consumption.Food Sci Nutr. 2018 Jun 1;6(6):1341-1351. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.694. eCollection 2018 Sep. Food Sci Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30258574 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boyde A. Staining plastic blocks with triiodide to image cells and soft tissues in backscattered electron SEM of skeletal and dental tissues. Eur Cell Mater. 2012;24:154–160. - PubMed
-
- Boyde A, Franc F. Freeze-drying shrinkage of glutaraldehyde fixed liver. J Microsc. 1981;122:75–86. - PubMed
-
- Boyde A, Koole LH. Embed in an iodinated polymer: A new paradigm for histology via backscattered electron imaging. J Anat. 2001;199:217–227.
-
- Chapman RF. The insects: Structure and function. Cambridge, UK. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 1998. Head; pp. 3–10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

