BDNF Val66met and 5-HTTLPR polymorphisms predict a human in vivo marker for brain serotonin levels
- PMID: 25220079
- PMCID: PMC6869129
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.22630
BDNF Val66met and 5-HTTLPR polymorphisms predict a human in vivo marker for brain serotonin levels
Abstract
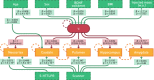
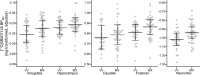
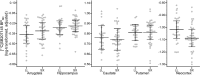
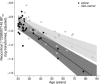
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) has been implicated in multiple aspects of brain function including regulation of serotonin signaling. The BDNF val66met polymorphism (rs6265) has been linked to aspects of serotonin signaling in humans but its effects are not well understood. To address this, we evaluated whether BDNF val66met was predictive of a putative marker of brain serotonin levels, serotonin 4 receptor (5-HT4 ) binding assessed with [11C]SB207145 positron emission tomography, which has also been associated with the serotonin-transporter-linked polymorphic region (5-HTTLPR) polymorphism. We applied a linear latent variable model (LVM) using regional 5-HT4 binding values (neocortex, amygdala, caudate, hippocampus, and putamen) from 68 healthy humans, allowing us to explicitly model brain-wide and region-specific genotype effects on 5-HT4 binding. Our data supported an LVM wherein BDNF val66met significantly predicted a LV reflecting [11C]SB207145 binding across regions (P = 0.005). BDNF val66met met-carriers showed 2-9% higher binding relative to val/val homozygotes. In contrast, 5-HTTLPR did not predict the LV but S-carriers showed 7% lower neocortical binding relative to LL homozygotes (P = 7.3 × 10(-6)). We observed no evidence for genetic interaction. Our findings indicate that BDNF val66met significantly predicts a common regulator of brain [11C]SB207145 binding, which we hypothesize reflects brain serotonin levels. In contrast, our data indicate that 5-HTTLPR specifically affects 5-HT4 binding in the neocortex. These findings implicate serotonin signaling as an important molecular mediator underlying the effects of BDNF val66met and 5-HTTLPR on behavior and related risk for neuropsychiatric illness in humans.
Keywords: 5-HT4 receptor; 5-HTTLPR; BDNF; positron emission tomography; serotonin.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BDNF val66met association with serotonin transporter binding in healthy humans.Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Feb 14;7(2):e1029. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.295. Transl Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28195567 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the impact of BDNF Val66Met genotype on serotonin transporter and serotonin-1A receptor binding.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 4;9(9):e106810. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106810. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25188405 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral 5-HT2A receptor and serotonin transporter binding in humans are not affected by the val66met BDNF polymorphism status or blood BDNF levels.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010 Nov;30(11):e1-7. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.114. Epub 2010 Aug 25. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010. PMID: 20736957 Free PMC article.
-
A Meta-Analysis of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Effects on Brain Volume in Schizophrenia: Genotype and Serum Levels.Neuropsychobiology. 2021;80(5):411-424. doi: 10.1159/000514126. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Neuropsychobiology. 2021. PMID: 33706323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF: New Views of an Old Player in Traumatic Brain Injury.Neuroscientist. 2024 Oct;30(5):560-573. doi: 10.1177/10738584231164918. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Neuroscientist. 2024. PMID: 37067029 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serotonin 4 Receptor Brain Binding in Major Depressive Disorder and Association With Memory Dysfunction.JAMA Psychiatry. 2023 Apr 1;80(4):296-304. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.4539. JAMA Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36753296 Free PMC article.
-
High trait aggression in men is associated with low 5-HT levels, as indexed by 5-HT4 receptor binding.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016 Apr;11(4):548-55. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsv140. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26772668 Free PMC article.
-
Epistasis of HTR1A and BDNF risk genes alters cortical 5-HT1A receptor binding: PET results link genotype to molecular phenotype in depression.Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Jan 16;9(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0308-2. Transl Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30664620 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin 4 receptor brain binding and oxytocin-promoted affective and social cognition in healthy women - A randomized controlled trial.Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2024 Jan 5;17:100224. doi: 10.1016/j.cpnec.2023.100224. eCollection 2024 Feb. Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38288372 Free PMC article.
-
Translational Genomic Research: The Association between Genetic Profiles and Cognitive Functioning or Cardiac Function Among Breast Cancer Survivors Completing Chemotherapy.Biol Res Nurs. 2022 Oct;24(4):433-447. doi: 10.1177/10998004221094386. Epub 2022 May 2. Biol Res Nurs. 2022. PMID: 35499926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arias B, Aguilera M, Moya J, Saiz PA, Villa H, Ibanez MI, Garcia‐Portillo MP, Bobes J, Ortet G, Fananas L (2012): The role of genetic variability in the SLC6A4, BDNF and GABRA6 genes in anxiety‐related traits. Acta Psychiatr Scand 125:194–202. - PubMed
-
- Comtat C, Sureau FC, Sibomana M, Hong IK, Sjoholm N, Trebossen R (2008) Image based resolution modeling for the HRRT OSEM reconstructions software. In: IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, NSS′08. Dresden, Germany. pp 4120–4123.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

