Chibby functions in Xenopus ciliary assembly, embryonic development, and the regulation of gene expression
- PMID: 25220153
- PMCID: PMC4539557
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.09.008
Chibby functions in Xenopus ciliary assembly, embryonic development, and the regulation of gene expression
Abstract
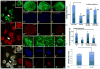
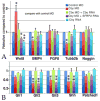
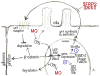
Wnt signaling and ciliogenesis are core features of embryonic development in a range of metazoans. Chibby (Cby), a basal-body associated protein, regulates β-catenin-mediated Wnt signaling in the mouse but not Drosophila. Here we present an analysis of Cby's embryonic expression and morphant phenotypes in Xenopus laevis. Cby RNA is supplied maternally, negatively regulated by Snail2 but not Twist1, preferentially expressed in the neuroectoderm, and regulates β-catenin-mediated gene expression. Reducing Cby levels reduced the density of multiciliated cells, the number of basal bodies per multiciliated cell, and the numbers of neural tube primary cilia; it also led to abnormal development of the neural crest, central nervous system, and pronephros, all defects that were rescued by a Cby-GFP chimera. Reduction of Cby led to an increase in Wnt8a and decreases in Gli2, Gli3, and Shh RNA levels. Many, but not all, morphant phenotypes were significantly reversed by the Wnt inhibitor SFRP2. These observations extend our understanding of Cby's role in mediating the network of interactions between ciliogenesis, signaling systems and tissue patterning.
Keywords: Chibby; Cilia; Hedgehog; Neural crest; Neural plate; Pronephros; Snail2; Wnt signaling; Xenopus laevis.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Ariizumi T, Takahashi S, Chan TC, Ito Y, Michiue T, Asashima M. Isolation and differentiation of Xenopus animal cap cells. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol. 2009;Chapter 1(Unit 1D):5. - PubMed
-
- Bradley L, Sun B, Collins-Racie L, LaVallie E, McCoy J, Sive H. Different activities of the frizzled-related proteins frzb2 and sizzled2 during Xenopus anteroposterior patterning. Dev Biol. 2000;227(1):118–32. - PubMed
-
- Carl TF, Dufton C, Hanken J, Klymkowsky MW. Inhibition of Neural Crest Migration in Xenopus Using Antisense Slug RNA. Dev Biol. 1999;213(1):101–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

