Connecting teratogen-induced congenital heart defects to neural crest cells and their effect on cardiac function
- PMID: 25220155
- PMCID: PMC4238913
- DOI: 10.1002/bdrc.21082
Connecting teratogen-induced congenital heart defects to neural crest cells and their effect on cardiac function
Abstract
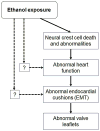
Neural crest cells play many key roles in embryonic development, as demonstrated by the abnormalities that result from their specific absence or dysfunction. Unfortunately, these key cells are particularly sensitive to abnormalities in various intrinsic and extrinsic factors, such as genetic deletions or ethanol-exposure that lead to morbidity and mortality for organisms. This review discusses the role identified for a segment of neural crest in regulating the morphogenesis of the heart and associated great vessels. The paradox is that their derivatives constitute a small proportion of cells to the cardiovascular system. Findings supporting that these cells impact early cardiac function raises the interesting possibility that they indirectly control cardiovascular development at least partially through regulating function. Making connections between insults to the neural crest, cardiac function, and morphogenesis is more approachable with technological advances. Expanding our understanding of early functional consequences could be useful in improving diagnosis and testing therapies.
Keywords: cardiac; physiology; cardiogenesis; folic acid; neural crest cells; optical coherence tomography; ethanol; prenatal alcohol exposure; teratogen.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare pertinent to this review.
Figures
References
-
- Abu-Issa R, Smyth G, Smoak I, Yamamura K, Meyers EN. Fgf8 is required for pharyngeal arch and cardiovascular development in the mouse. Development. 2002;129(19):4613–4625. - PubMed
-
- Adams MS, Bronner-Fraser M. Review: the role of neural crest cells in the endocrine system. Endocr Pathol. 2009;20(2):92–100. - PubMed
-
- Adickes ED, Mollner TJ, Makoid MC. Ethanol-induced teratogenic alterations in developing cardiomyocytes in culture. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl. 1993;2:283–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

