Pig-to-monkey islet xenotransplantation using multi-transgenic pigs
- PMID: 25220221
- PMCID: PMC4169326
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.12868
Pig-to-monkey islet xenotransplantation using multi-transgenic pigs
Abstract
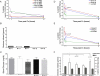
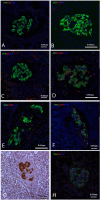
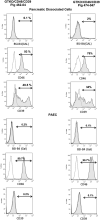
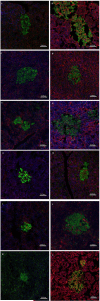
The generation of pigs with genetic modifications has significantly advanced the field of xenotransplantation. New genetically engineered pigs were produced on an α1,3-galactosyltransferase gene-knockout background with ubiquitous expression of human CD46, with islet beta cell-specific expression of human tissue factor pathway inhibitor and/or human CD39 and/or porcine CTLA4-lg. Isolated islets from pigs with 3, 4 or 5 genetic modifications were transplanted intraportally into streptozotocin-diabetic, immunosuppressed cynomolgus monkeys (n = 5). Immunosuppression was based on anti-CD154 mAb costimulation blockade. Monitoring included features of early islet destruction, glycemia, exogenous insulin requirement and histopathology of the islets at necropsy. Using these modified pig islets, there was evidence of reduced islet destruction in the first hours after transplantation, compared with two series of historical controls that received identical therapy but were transplanted with islets from pigs with either no or only one genetic modification. Despite encouraging effects on early islet loss, these multi-transgenic islet grafts did not demonstrate consistency in regard to long-term success, with only two of five demonstrating function beyond 5 months.
Keywords: Translational research/science; islets of Langerhans; nonhuman primate; xenotransplantation.
© Copyright 2014 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures

References
-
- Ekser B, Ezzelarab M, Hara H, van der Windt DJ, Wijkstrom M, Bottino R, et al. Clinical xenotransplantation: the next medical revolution? Lancet. 2012;379:672–683. - PubMed
-
- Cooper DKC, Bottino R, Satyananda V, Wijkstrom M, Trucco M. Toward clinical islet xenotransplantation – are revisions to the IXA guidelines warranted? Xenotransplantation. 2013;2:68–74. - PubMed
-
- Dufrane D, Gianello P. Pig islet xenotransplantation in human: structural and physiological compatibility for human clinical application. Transplant Rev. 2012;26:183–188. - PubMed
-
- Elliott RB. Towards xenotransplantation of pig islets in the clinic. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2011;16:195–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

