Critical role of NKT cells in posttransplant alloantibody production
- PMID: 25220596
- PMCID: PMC4207222
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.12922
Critical role of NKT cells in posttransplant alloantibody production
Abstract
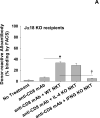
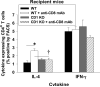
We previously reported that posttransplant alloantibody production in CD8-deficient hosts is IL-4+ CD4+ T cell-dependent and IgG1 isotype-dominant. The current studies investigated the hypothesis that IL-4-producing natural killer T cells (NKT cells) contribute to maximal alloantibody production. To investigate this, alloantibody levels were examined in CD8-deficient WT, CD1d KO and Jα18 KO transplant recipients. We found that the magnitude of IgG1 alloantibody production was critically dependent on the presence of type I NKT cells, which are activated by day 1 posttransplant. Unexpectedly, type I NKT cell contribution to enhanced IgG1 alloantibody levels was interferon-γ-dependent and IL-4-independent. Cognate interactions between type I NKT and B cells alone do not stimulate alloantibody production. Instead, NKT cells appear to enhance maturation of IL-4+ CD4+ T cells. To our knowledge, this is the first report to substantiate a critical role for type I NKT cells in enhancing in vivo antibody production in response to endogenous antigenic stimuli.
© Copyright 2014 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures



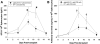


References
-
- McKenna RM, Takemoto SK, Terasaki PI. Anti-HLA antibodies after solid organ transplantation. Transplantation. 2000;69(3):319–326. - PubMed
-
- Lorenz M, Regele H, Schillinger M, Exner M, Rasoul-Rockenschaub S, Wahrmann M, et al. Risk factors for capillary C4d deposition in kidney allografts: evaluation of a large study cohort. Transplantation. 2004;78(3):447–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

