Exosome proteomics reveals transcriptional regulator proteins with potential to mediate downstream pathways
- PMID: 25220623
- PMCID: PMC4454399
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12534
Exosome proteomics reveals transcriptional regulator proteins with potential to mediate downstream pathways
Abstract
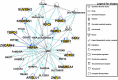
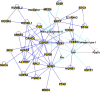
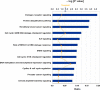
Exosomes are virus-sized, membrane-enclosed vesicles with origins in the cellular endosomal system, but are released extracellularly. As a population, these tiny vesicles carry relatively enormous amounts of information in their protein, lipid and nucleic acid content, and the vesicles can have profound impacts on recipient cells. This review employs publically-available data combined with gene ontology applications to propose a novel concept, that exosomes transport transcriptional and translational machinery that may have direct impacts on gene expression in recipient cells. Here, we examine the previously published proteomic contents of medulloblastoma-derived exosomes, focusing on transcriptional regulators; we found that there are numerous proteins that may have potential roles in transcriptional and translational regulation with putative influence on downstream, cancer-related pathways. We expanded this search to all of the proteins in the Vesiclepedia database; using gene ontology approaches, we see that these regulatory factors are implicated in many of the processes involved in cancer initiation and progression. This information suggests that some of the effects of exosomes on recipient cells may be due to the delivery of protein factors that can directly and fundamentally change the transcriptional landscape of the cells. Within a tumor environment, this has potential to tilt the advantage towards the cancer.
Keywords: Cancer; exosomes; gene ontology; proteomics; transcriptional regulators.
© 2014 The Authors. Cancer Science published by Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Medulloblastoma exosome proteomics yield functional roles for extracellular vesicles.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e42064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042064. Epub 2012 Jul 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22848702 Free PMC article.
-
Two distinct populations of exosomes are released from LIM1863 colon carcinoma cell-derived organoids.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Mar;12(3):587-98. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.021303. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23230278 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes as carriers transporting long non‑coding RNAs: Molecular characteristics and their function in cancer (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2019 Aug;20(2):851-862. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10340. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31173220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Proteomics Analysis Reveals a Secretory Path- and Status-Dependent Signature of Exosomes Released from Tumor-Associated Macrophages.J Proteome Res. 2015 Oct 2;14(10):4319-31. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00770. Epub 2015 Sep 8. J Proteome Res. 2015. PMID: 26312558
-
Challenges in the Isolation and Proteomic Analysis of Cancer Exosomes-Implications for Translational Research.Proteomes. 2019 May 15;7(2):22. doi: 10.3390/proteomes7020022. Proteomes. 2019. PMID: 31096692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ontologies and Knowledge Graphs in Oncology Research.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 10;14(8):1906. doi: 10.3390/cancers14081906. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Exchange of Lung-Derived Exosome to Brain Causing Neuronal Changes on COVID-19 Infection.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Oct;58(10):5356-5368. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02485-9. Epub 2021 Jul 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34312772 Free PMC article.
-
YBX-1 mediated sorting of miR-133 into hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced EPC-derived exosomes to increase fibroblast angiogenesis and MEndoT.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Aug 23;10(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1377-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31443679 Free PMC article.
-
HDGF enhances VEGF‑dependent angiogenesis and FGF‑2 is a VEGF‑independent angiogenic factor in non‑small cell lung cancer.Oncol Rep. 2020 Jul;44(1):14-28. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7580. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32319650 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer nanotechnology: current status and perspectives.Nano Converg. 2021 Nov 2;8(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s40580-021-00282-7. Nano Converg. 2021. PMID: 34727233 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Simpson RJ, Jensen SS, Lim JW. Proteomic profiling of exosomes: current perspectives. Proteomics. 2008;8:4083–99. - PubMed
-
- Nickel W, Rabouille C. Mechanisms of regulated unconventional protein secretion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:148–55. - PubMed
-
- Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, Orr L, Turbide C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes) J Biol Chem. 1987;262:9412–20. - PubMed
-
- Simons M, Raposo G. Exosomes-Vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21:575–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

