Novel antiproliferative chimeric compounds with marked histone deacetylase inhibitory activity
- PMID: 25221651
- PMCID: PMC4160757
- DOI: 10.1021/ml5000959
Novel antiproliferative chimeric compounds with marked histone deacetylase inhibitory activity
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Novel Antiproliferative Chimeric Compounds with Marked Histone Deacetylase Inhibitory Activity".ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024 Jul 3;15(8):1402. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.4c00301. eCollection 2024 Aug 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024. PMID: 39140074 Free PMC article.
Abstract
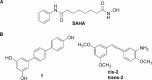
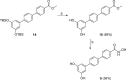
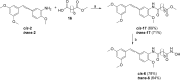
Given our interest in finding potential antitumor agents and in view of the multifactorial mechanistic nature of cancer, in the present work, taking advantage of the multifunctional ligands approach, new chimeric molecules were designed and synthesized by combining in single chemical entities structural features of SAHA, targeting histone deacetylases (HDACs), with substituted stilbene or terphenyl derivatives previously obtained by us and endowed with antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic activity. The new chimeric derivatives were characterized with respect to their cytotoxic activity and their effects on cell cycle progression on different tumor cell lines, as well as their HDACs inhibition. Among the other, trans -6 showed the most interesting biological profile, as it exhibited a strong pro-apoptotic activity in tumor cell lines in comparison with both of its parent compounds and a marked HDAC inhibition.
Keywords: HDAC inhibition; Multifunctional ligands; antiproliferative activity; chimeric compound; stilbene.
Figures




References
-
- Hanahan D.; Weinberg R. A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. - PubMed
-
- Morphy R.; Kay C.; Rankovic Z. From magic bullets to designed multiple ligands. Drug Discovery Today 2004, 9, 641–651. - PubMed
-
- Morphy R.; Rankovic Z. Designing multiple ligands: medicinal chemistry strategies and challenges. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 587–600. - PubMed
-
- Peters J. U. Polypharmacology: foe or friend?. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8955–8971. - PubMed
-
- Nebbioso A.; Pereira R.; Khanwalkar H.; Matarese F.; Garcìa-Rodrìguez J.; Miceli M.; Logie C.; Kedinger V.; Ferrara F.; Stunnenberg H. G.; De Lera A. R.; Gronemeyer H.; Altucci L. Death receptor pathway activation and increase of ROS production by the triple epigenetic inhibitor UVI5008. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2394–2404. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

