Collagenous colitis associated with protein losing enteropathy in a toddler
- PMID: 25221677
- PMCID: PMC4158112
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/209624
Collagenous colitis associated with protein losing enteropathy in a toddler
Abstract
Collagenous mucosal inflammatory disease is a rare gastrointestinal disorder that involves the columnar lining of gastric and intestinal mucosa and is characterized by a distinct subepithelial collagen deposition. Recent clinical and pathological evidence have indicated that collagenous mucosal inflammatory disease can be extensive disease that may concomitantly involve several gastrointestinal sites at the same time. This entity, however, occurs infrequently in children. It is even less common to find concomitant depositions of collagen in the mucosa of gastrointestinal sites other than the colon. Only two cases in pediatric literature reported concomitant involvement, one with gastric and colonic involvement and the other one with gastroduodenocolitis. We are reporting a 15-month-old boy who presented with severe diarrhea and diffuse edema secondary to hypoalbuminemia. Further testing documented protein losing enteropathy (PLE) associated with collagenous colitis.
Figures
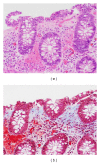
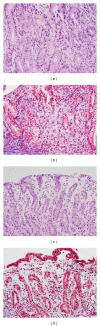
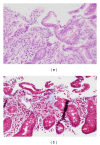
References
-
- Freeman HJ. Collagenous mucosal inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 2005;129(1):338–350. - PubMed
-
- Lindstrom CG. Collagenous colitis' with watery diarrhoea—a new entity? Pathologia Europaea. 1976;11(1):87–89. - PubMed
-
- Esselinckx W, Brenard R, Colin JF, Melange M. Juvenile scleroderma and collagenous colitis. The first case. Journal of Rheumatology. 1989;16(6):834–836. - PubMed
-
- Busuttil A. Collagenous colitis in a child. The American Journal of Diseases of Children. 1989;143(9):998–1000. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

