A review of web based interventions focusing on alcohol use
- PMID: 25221690
- PMCID: PMC4160666
- DOI: 10.4103/2141-9248.139272
A review of web based interventions focusing on alcohol use
Abstract
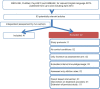
Alcohol continues to be a major contributor to morbidity and mortality globally. Despite the scientific advances, alcohol use related problems continue to pose a major challenge to medicine and public health. Internet offers a new mode to provide health care interventions. Web based interventions (WBIs) provide the health care services at the door steps of the end users. WBIs have been developed for alcohol use related problems over the past few years. WBIs offer a potentially relevant and viable mode of service delivery to problem alcohol users. Hence, it is important to assess these interventions for their effectiveness. Some of the existing WBIs for alcohol use assessed systematically in controlled trials. The current review evaluates the available evidence for the effectiveness of WBIs for reducing alcohol use. The literature search was performed using MedLine, PubMed, PsycINFO and EMBASE for relevant English language articles published up to and including April 2013. Only publications focused on reducing alcohol use through WBIs were included.
Keywords: Alcohol; Internet; Interventions; Web based.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Balhara YP, Mathur S. Alcohol: A major public health problem-South Asian perspective. Addict Dis Treatment. 2012;11:101–20.
-
- Room R, Babor T, Rehm J. Alcohol and public health. Lancet. 2005;365:519–30. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham JA, Blomqvist J. Examining treatment use among alcohol-dependent individuals from a population perspective. Alcohol Alcohol. 2006;41:632–5. - PubMed
-
- Flay BR, Biglan A, Boruch RF, Castro FG, Gottfredson D, Kellam S, et al. Standards of evidence: Criteria for efficacy, effectiveness and dissemination. Prev Sci. 2005;6:151–75. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous