Deciphering Fur transcriptional regulatory network highlights its complex role beyond iron metabolism in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 25222563
- PMCID: PMC4167408
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5910
Deciphering Fur transcriptional regulatory network highlights its complex role beyond iron metabolism in Escherichia coli
Abstract
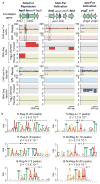
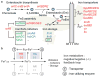
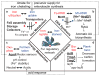
The ferric uptake regulator (Fur) plays a critical role in the transcriptional regulation of iron metabolism. However, the full regulatory potential of Fur remains undefined. Here we comprehensively reconstruct the Fur transcriptional regulatory network in Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 in response to iron availability using genome-wide measurements. Integrative data analysis reveals that a total of 81 genes in 42 transcription units are directly regulated by three different modes of Fur regulation, including apo- and holo-Fur activation and holo-Fur repression. We show that Fur connects iron transport and utilization enzymes with negative-feedback loop pairs for iron homeostasis. In addition, direct involvement of Fur in the regulation of DNA synthesis, energy metabolism and biofilm development is found. These results show how Fur exhibits a comprehensive regulatory role affecting many fundamental cellular processes linked to iron metabolism in order to coordinate the overall response of E. coli to iron availability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


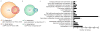
References
-
- Andrews SC, Robinson AK, Rodriguez-Quinones F. Bacterial iron homeostasis. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2003;27:215–237. - PubMed
-
- Delany I, Rappuoli R, Scarlato V. Fur functions as an activator and as a repressor of putative virulence genes in Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 2004;52:1081–1090. - PubMed
-
- Nandal A, et al. Induction of the ferritin gene (ftnA) of Escherichia coli by Fe(2+)-Fur is mediated by reversal of H-NS silencing and is RyhB independent. Mol Microbiol. 2010;75:637–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

