Pharmacokinetics and concentration-effect relationship of adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 25223394
- PMCID: PMC4309634
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12509
Pharmacokinetics and concentration-effect relationship of adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Aims: This study aimed at describing adalimumab pharmacokinetics (PK) and the concentration-effect relationship of adalimumab using pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) modelling in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
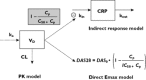
Methods: Adalimumab PK and PK-PD data were obtained from a multicentric observational study. Adalimumab (40 mg) was administered subcutaneously every other week, and its pharmacokinetics was described using a one-compartment model. The relationship between adalimumab concentration and C-reactive protein (CRP) concentration was described using an indirect response model with inhibition of CRP input, whereas the relationship between adalimumab concentration and disease activity score in 28 joints (DAS28) was described using a direct inhibition model. Dose regimens that included a loading dose of adalimumab were simulated.
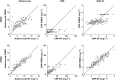
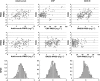
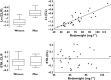
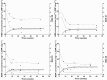
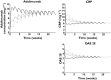
Results: Thirty patients treated for RA were analysed. The following pharmacokinetic and PK-PD parameters were estimated (interidividual coefficient of variation): apparent volume of distribution (Vd /F) = 10.8 l (92%); apparent clearance (CL/F) = 0.32 l day(-1) (17%); first-order absorption rate (ka ) = 0.28 day(-1) ; CRP input (kin ) = 22.0 mg l(-1) day(-1) (65%); adalimumab concentration leading to a 50% decrease in kin (C50 ) = 3.6 mg l(-1) (88%); baseline DAS28 (DAS0 ) = 5.5 mg l(-1) (11%); and adalimumab concentration leading to 50% decrease of DAS0 (IC50 ) = 11.0 mg l(-1) (71%). Simulations showed that a 160 mg loading dose should reduce the time to reach efficacy in terms of both CRP and DAS28 after the first injection.
Conclusions: This is the first study to describe adalimumab pharmacokinetics and the concentration-effect relationship in RA. A 160 mg loading dose may lead to an increased benefit from treatment in RA patients.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00234234.
Keywords: adalimumab; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling; pharmacokinetics; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- FDA. 2011. Adalimumab indications and usage. Accessed at http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsar... (last accessed 16 October 2014).
-
- Bartelds GM, Krieckaert CL, Nurmohamed MT, van Schouwenburg PA, Lems WF, Twisk JW, Dijkmans BA, Aarden L, Wolbink GJ. Development of antidrug antibodies against adalimumab and association with disease activity and treatment failure during long-term follow-up. JAMA. 2011;305:1460–1468. - PubMed
-
- Hanauer SB, Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, Fedorak RN, Lukas M, MacIntosh D, Panaccione R, Wolf D, Pollack P. Human anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody (adalimumab) in Crohn's disease: the CLASSIC-I trial. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:323–333. quiz 591. - PubMed
-
- van de Putte LB, Atkins C, Malaise M, Sany J, Russell AS, van Riel PL, Settas L, Bijlsma JW, Todesco S, Dougados M, Nash P, Emery P, Walter N, Kaul M, Fischkoff S, Kupper H. Efficacy and safety of adalimumab as monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis for whom previous disease modifying antirheumatic drug treatment has failed. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63:508–516. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

