Effects of PDE4 pathway inhibition in rat experimental stroke
- PMID: 25224348
- PMCID: PMC4364446
- DOI: 10.18433/j3s02v
Effects of PDE4 pathway inhibition in rat experimental stroke
Abstract
Purpose: The first genomewide association study indicated that variations in the phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) gene confer risk for ischemic stroke. However, inconsistencies among the studies designed to replicate the findings indicated the need for further investigation to elucidate the role of the PDE4 pathway in stroke pathogenesis. Hence, we studied the effect of global inhibition of the PDE4 pathway in two rat experimental stroke models, using the PDE4 inhibitor rolipram. Further, the specific role of the PDE4D isoform in ischemic stroke pathogenesis was studied using PDE4D knockout rats in experimental stroke.
Methods: Rats were subjected to either the ligation or embolic stroke model and treated with rolipram (3mg/kg; i.p.) prior to the ischemic insult. Similarly, the PDE4D knockout rats were subjected to experimental stroke using the embolic model.
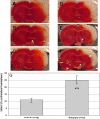
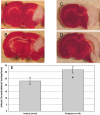
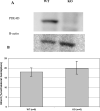
Results: Global inhibition of the PDE4 pathway using rolipram produced infarcts that were 225% (p<0.01) and 138% (p<0.05) of control in the ligation and embolic models, respectively. PDE4D knockout rats subjected to embolic stroke showed no change in infarct size compared to wild-type control.
Conclusions: Despite increase in infarct size after global inhibition of the PDE4 pathway with rolipram, specific inhibition of the PDE4D isoform had no effect on experimental stroke. These findings support a role for the PDE4 pathway, independent of the PDE4D isoform, in ischemic stroke pathogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The unrecognized effects of phosphodiesterase 4 on epithelial cells in pulmonary inflammation.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 24;10(4):e0121725. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121725. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25909327 Free PMC article.
-
Rolipram suppresses migration and invasion of human choriocarcinoma cells by inhibiting phosphodiesterase 4-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023 Jul;37(7):e23363. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23363. Epub 2023 Apr 5. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37020384
-
Antidepressant-like profile and reduced sensitivity to rolipram in mice deficient in the PDE4D phosphodiesterase enzyme.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002 Oct;27(4):587-95. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00344-5. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002. PMID: 12377395
-
Targeting phosphodiesterase 4 as a potential therapeutic strategy for enhancing neuroplasticity following ischemic stroke.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Oct 3;14(12):1745-1754. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.26230. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30416389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphodiesterase4D (PDE4D)--A risk factor for atrial fibrillation and stroke?J Neurol Sci. 2015 Dec 15;359(1-2):266-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2015.11.010. Epub 2015 Nov 11. J Neurol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26671126 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroinflammation in Ischemic Stroke: Inhibition of cAMP-Specific Phosphodiesterases (PDEs) to the Rescue.Biomedicines. 2021 Jun 22;9(7):703. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070703. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34206420 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Della-Morte D, Guadagni F, Palmirotta R, Testa G, Caso V, Paciaroni M, Abete P, Rengo F, Ferroni P, Sacco RL, Rundek T. Genetics of ischemic stroke, stroke-related risk factors, stroke precursors and treatments. Pharmacogenomics. 2012;13(5):595–613. - PubMed
-
- Gretarsdottir S, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir ST, Manolescu A, Jonsdottir S, Jonsdottir T, Gudmundsdottir T, Bjarnadottir SM, Einarsson OB, Gudjonsdottir HM, Hawkins M, Gudmundsson G, Gudmundsdottir H, Andrason H, Gudmundsdottir AS, Sigurdardottir M, Chou TT, Nahmias J, Goss S, Sveinbjörnsdottir S, Valdimarsson EM, Jakobsson F, Agnarsson U, Gudnason V, Thorgeirsson G, Fingerle J, Gurney M, Gudbjartsson D, Frigge ML, Kong A, Stefansson K, Gulcher JR. The gene encoding phosphodiesterase 4D confers risk of ischemic stroke. Nat Genet. 2003;35(2):131–138. - PubMed
-
- Munshi A, Babu MS, Kaul S, Shafi G, Anila AN, Alladi S, Jyothy A. Phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) gene variants and the risk of ischemic stroke in a South Indian population. J Neurol Sci. 2009;285:142–145. - PubMed
-
- Saleheen D, Bukhari S, Haider SR, Nazir A, Khanum S, Shafqat S, Anis MK, Frossard P. Association of phosphodiesterase 4D gene with ischemic stroke in a Pakistani population. Stroke. 2005;36(10):2275–2277. - PubMed
