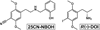
Hallucinogen-like effects of 2-([2-(4-cyano-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl) ethylamino]methyl)phenol (25CN-NBOH), a novel N-benzylphenethylamine with 100-fold selectivity for 5-HT₂A receptors, in mice
- PMID: 25224567
- PMCID: PMC4339409
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-014-3739-3
Hallucinogen-like effects of 2-([2-(4-cyano-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl) ethylamino]methyl)phenol (25CN-NBOH), a novel N-benzylphenethylamine with 100-fold selectivity for 5-HT₂A receptors, in mice
Abstract
Rationale: 2-([2-(4-cyano-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethylamino]methyl)phenol (25CN-NBOH) is structurally similar to N-benzyl substituted phenethylamine hallucinogens currently emerging as drugs of abuse. 25CN-NBOH exhibits dramatic selectivity for 5-HT2A receptors in vitro, but has not been behaviorally characterized.
Objective: 25CN-NBOH was compared to the traditional phenethylamine hallucinogen R(-)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine (DOI) using mouse models of drug-elicited head twitch behavior and drug discrimination.
Methods: Drug-elicited head twitches were quantified for 10 min following administration of various doses of either DOI or 25CN-NBOH, with and without pretreatments of 0.01 mg/kg 5-HT2A antagonist M100907 or 3.0 mg/kg 5-HT2C antagonist RS102221. The capacity of 25CN-NBOH to attenuate DOI-elicited head twitch was also investigated. Mice were trained to discriminate DOI or M100907 from saline, and 25CN-NBOH was tested for generalization.
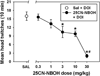
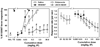
Results: 25CN-NBOH induced a head twitch response in the mouse that was lower in magnitude than that of DOI, blocked by M100907, but not altered by RS102221. DOI-elicited head twitch was dose-dependently attenuated by 25CN-NBOH pretreatment. 25CN-NBOH produced an intermediate degree of generalization (55 %) for the DOI training dose, and these interoceptive effects were attenuated by M100907. Finally, 25CN-NBOH did not generalize to M100907 at any dose, but ketanserin fully substituted in these animals.
Conclusions: 25CN-NBOH was behaviorally active, but less effective than DOI in two mouse models of hallucinogenic effects. The effectiveness with which M100907 antagonized the behavioral actions of 25CN-NBOH strongly suggests that the 5-HT2A receptor is an important site of agonist action for this compound in vivo.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chronic treatment with a metabotropic mGlu2/3 receptor agonist diminishes behavioral response to a phenethylamine hallucinogen.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Feb;236(2):821-830. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5118-y. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30448990 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors in R(-)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine-elicited head twitch behavior in mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Dec;335(3):728-34. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.172247. Epub 2010 Sep 21. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20858706 Free PMC article.
-
Hallucinogen-like actions of 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(n)-propylthiophenethylamine (2C-T-7) in mice and rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Sep;181(3):496-503. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0009-4. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15983786
-
25CN-NBOH: A Selective Agonist for in vitro and in vivo Investigations of the Serotonin 2A Receptor.ChemMedChem. 2021 Nov 5;16(21):3263-3270. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202100395. Epub 2021 Aug 21. ChemMedChem. 2021. PMID: 34288515 Review.
-
Effect of Hallucinogens on Unconditioned Behavior.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;36:159-199. doi: 10.1007/7854_2016_466. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28224459 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of a Hallucinogen-Activated Gq-Coupled 5-HT2A Serotonin Receptor.Cell. 2020 Sep 17;182(6):1574-1588.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.024. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32946782 Free PMC article.
-
Psychedelics.Pharmacol Rev. 2016 Apr;68(2):264-355. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.011478. Pharmacol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26841800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DARK Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: NBOMes.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020 Dec 2;11(23):3860-3869. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00528. Epub 2019 Nov 12. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31657895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
25I-NBOH: a new potent serotonin 5-HT2A receptor agonist identified in blotter paper seizures in Brazil.Forensic Toxicol. 2017;35(2):408-414. doi: 10.1007/s11419-017-0357-x. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Forensic Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28706567 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative neuropharmacology of N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (NBOMe) hallucinogens and their 2C counterparts in male rats.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Nov;142:240-250. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.02.033. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29501528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD) “NBOMe” compounds: A review of the evidence of use and harm. [Accessed 03 July 2014];2013 Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/fil....
-
- Blaazer AR, Smid P, Kruse CG. Structure-activity relationships of phenylalkylamines as agonist ligands for 5-HT(2A) receptors. Chem Med Chem. 2008;3(9):1299–1309. - PubMed
-
- Braden MR, Parrish JC, Naylor JC, Nichols DE. Molecular interaction of serotonin 5-HT2A receptor residues Phe339(6.51) and Phe340(6.52) with superpotent N-benzyl phenethylamine agonists. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;70(6):1956–1964. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

