Parent-offspring similarity for drinking: a longitudinal adoption study
- PMID: 25224596
- PMCID: PMC4439100
- DOI: 10.1007/s10519-014-9672-8
Parent-offspring similarity for drinking: a longitudinal adoption study
Abstract
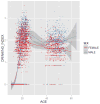
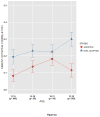
Parent-offspring resemblance for drinking was investigated in a sample of 409 adopted and 208 non-adopted families participating in the Sibling Interaction and Behavior Study. Drinking data was available for 1,229 offspring, assessed longitudinally up to three times in the age range from 10 to 28 years. A single drinking index was computed from four items measuring quantity, frequency and density of drinking. As expected, the mean drinking index increased with age, was greater in males as compared to females (although not at the younger ages), but did not vary significantly by adoption status. Parent-offspring correlation in drinking did not vary significantly by either offspring or parent gender but did differ significantly by adoption status. In adopted families, the parent-offspring correlation was statistically significant at all ages but decreased for the oldest age group (age 22-28). In non-adopted families, the parent-offspring correlation was statistically significant at all ages and increased in the oldest age group. Findings imply that genetic influences on drinking behavior increase with age while shared family environment influences decline, especially during the transition from late-adolescence to early adulthood.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Parent and sibling influences on adolescent alcohol use and misuse: evidence from a U.S. adoption cohort.J Stud Alcohol. 1996 Jan;57(1):8-18. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1996.57.8. J Stud Alcohol. 1996. PMID: 8747496
-
General and specific predictors of nicotine and alcohol dependence in early adulthood: genetic and environmental influences.J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2014 Jul;75(4):623-34. doi: 10.15288/jsad.2014.75.623. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24988261 Free PMC article.
-
Parent-Offspring Resemblance for Drinking Behaviors in a Longitudinal Twin Sample.J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2017 Jan;78(1):49-58. doi: 10.15288/jsad.2017.78.49. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2017. PMID: 27936364 Free PMC article.
-
Sources of Parent-Offspring Resemblance for Major Depression in a National Swedish Extended Adoption Study.JAMA Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 1;75(2):194-200. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.3828. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29238796 Free PMC article.
-
Natural cohorts: family similarity in adult cognition.Nebr Symp Motiv. 1991;39:205-43. Nebr Symp Motiv. 1991. PMID: 1843136
Cited by
-
Testing the effects of adolescent alcohol use on adult conflict-related theta dynamics.Clin Neurophysiol. 2017 Nov;128(11):2358-2368. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2017.08.019. Epub 2017 Sep 9. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28935223 Free PMC article.
-
Problematic alcohol use and hippocampal volume in a female sample: disentangling cause from consequence using a co-twin control study design.Psychol Med. 2018 Jul;48(10):1673-1684. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717003166. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Psychol Med. 2018. PMID: 29108528 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal stability and change in time-frequency measures from an oddball task during adolescence and early adulthood.Psychophysiology. 2023 Mar;60(3):e14200. doi: 10.1111/psyp.14200. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Psychophysiology. 2023. PMID: 36281995 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between polygenic risk of substance use and use disorder and alcohol, cannabis, and nicotine use in adolescence and young adulthood in a longitudinal twin study.Psychol Med. 2023 Apr;53(6):2296-2306. doi: 10.1017/S0033291721004116. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Psychol Med. 2023. PMID: 37310313 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and environmental sources of covariation between early drinking and adult functioning.Psychol Addict Behav. 2017 Aug;31(5):589-600. doi: 10.1037/adb0000283. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Psychol Addict Behav. 2017. PMID: 28594187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bandura A. A sociocognitive analysis of substance abuse: An agentic perspective. [Article; Proceedings Paper] Psychological Science. 1999;10(3):214–217. doi: 10.1111/1467-9280.00138. - DOI
-
- Bergen SE, Gardner CO, Kendler KS. Age-related changes in heritability of behavioral phenotypes over adolescence and young adulthood: A meta-analysis. Twin Research and Human Genetics. 2007;10(3):423–433. - PubMed
-
- Dick DM, Prescott C, McGue M. Genetics of substance use and substance use disorders. In: Kim YK, editor. Handbook of Behavior Genetics. New York: Springer; 2009. pp. 433–454.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

