Different mechanisms of acute versus long-term antihypertensive effects of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition: studies in Cyp1a1-Ren-2 transgenic rats
- PMID: 25224811
- PMCID: PMC4347520
- DOI: 10.1111/1440-1681.12310
Different mechanisms of acute versus long-term antihypertensive effects of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition: studies in Cyp1a1-Ren-2 transgenic rats
Abstract
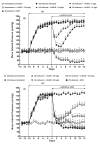
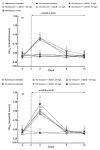
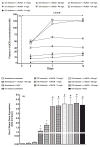
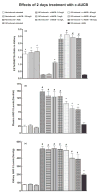
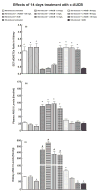
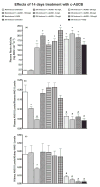
Recent studies have shown that the long-term antihypertensive action of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition (sEH) in angiotensin-II (AngII)-dependent hypertension might be mediated by the suppression of intrarenal AngII levels. To test this hypothesis, we examined the effects of acute (2 days) and chronic (14 days) sEH inhibition on blood pressure (BP) in transgenic rats with inducible AngII-dependent hypertension. AngII-dependent malignant hypertension was induced by 10 days' dietary administration of indole-3-carbinol (I3C), a natural xenobiotic that activates the mouse renin gene in Cyp1a1-Ren-2 transgenic rats. BP was monitored by radiotelemetry. Acute and chronic sEH inhibition was achieved using cis-4-(4-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)cyclohexyloxy) benzoic acid, given at doses of 0.3, 3, 13, 26, 60 and 130 mg/L in drinking water. At the end of experiments, renal concentrations of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, their inactive metabolites dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids and AngII were measured. Acute BP-lowering effects of sEH inhibition in I3C-induced rats was associated with a marked increase in renal epoxyeicosatrienoic acids to dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids ratio and acute natriuresis. Chronic treatment with cis-4-(4-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)cyclohexyloxy) benzoic acid in I3C-induced rats elicited dose-dependent persistent BP lowering associated with a significant reduction of plasma and kidney AngII levels. Our findings show that the acute BP-lowering effect of sEH inhibition in I3C-induced Cyp1a1-Ren-2 transgenic rats is mediated by a substantial increase in intrarenal epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and their natriuretic action without altering intrarenal renin-angiotensin system activity. Long-term antihypertensive action of cis-4-(4-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)cyclohexyloxy) benzoic acid in I3C-induced Cyp1a1-Ren-2 transgenic rats is mediated mostly by suppression of intrarenal AngII concentration.
Keywords: angiotensin-II; cytochrome P-450 epoxygenase; eicosanoids; epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; hypertension; soluble epoxide hydrolase.
© 2014 Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Roman RJ. P-450 metabolites of arachidonic acid in the control of cardiovascular function. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:131–185. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Carroll MA, Chander PN, Falck JR, Sangras B, Stier CT. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, AUDA, prevents early salt-sensitive hypertension. Front Biosci. 2008;13:3480–3487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

