Large animal models and new therapies for glycogen storage disease
- PMID: 25224826
- PMCID: PMC4513910
- DOI: 10.1007/s10545-014-9766-8
Large animal models and new therapies for glycogen storage disease
Abstract
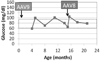
Glycogen storage diseases (GSD), a unique category of inherited metabolic disorders, were first described early in the twentieth century. Since then, the biochemical and genetic bases of these disorders have been determined, and an increasing number of animal models for GSD have become available. At least seven large mammalian models have been developed for laboratory research on GSDs. These models have facilitated the development of new therapies, including gene therapy, which are undergoing clinical translation. For example, gene therapy prolonged survival and prevented hypoglycemia during fasting for greater than one year in dogs with GSD type Ia, and the need for periodic re-administration to maintain efficacy was demonstrated in that dog model. The further development of gene therapy could provide curative therapy for patients with GSD and other inherited metabolic disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest:
Elizabeth Brooks declares that she has no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Angelos S, Valberg SJ, Smith BP, et al. Myophosphorylase deficiency associated with rhabdomyolysis and exercise intolerance in 6 related Charolais cattle. Musc Nerv. 1995;18(7):736–740. - PubMed
-
- Brix AE, Howerth EW, McConkie-Rosell A, et al. Glycogen storage disease type Ia in two littermate Maltese puppies. Vet Pathol. 1995;32(5):460–465. - PubMed
-
- Crane B, Luo X, Demaster A, et al. Rescue administration of a helper-dependent adenovirus vector with long-term efficacy in dogs with glycogen storage disease type Ia. Gene Ther. 2012;19(4):443–452. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham SC, Dane AP, Spinoulas A, Logan GJ, Alexander IE. Gene delivery to the juvenile mouse liver using AAV2/8 vectors. Mol Ther. 2008;16(6):1081–1088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

