Design, synthesis and characterization of fMLF-mimicking AApeptides
- PMID: 25224835
- PMCID: PMC4259043
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201402396
Design, synthesis and characterization of fMLF-mimicking AApeptides
Abstract
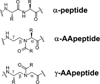
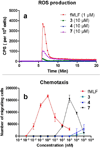
The tripeptide N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe (fMLF) is a potent neutrophil chemoattractant and the reference agonist for the G protein-coupled N-formylpeptide receptor (FPR). As it plays a very important role in host defense and inflammation, there has been considerable interest in the development of fMLF analogues in the hope of identifying potential therapeutic agents. Herein we report the design, synthesis, and evaluation of AApeptides that mimic the structure and function of fMLF. The lead AApeptides induced calcium mobilization and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signal transduction pathways in FPR-transfected rat basophilic leukemic (RBL) cells. More intriguingly, at high concentrations, certain AApeptides were more effective than fMLF in the induction of calcium mobilization. Their agonistic activity is further supported by their ability to stimulate chemotaxis and the production of superoxide in HL-60 cells. Similarly to fMLF, these AApeptides are much more selective towards FPR1 than FPR2. These results suggest that the fMLF-mimicking AApeptides might emerge as a new class of therapeutic agents that target FPRs.
Keywords: AApeptides; calcium; chemotaxis; fMLF; peptidomimetics.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
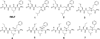

Similar articles
-
Structural determinants for the interaction of formyl peptide receptor 2 with peptide ligands.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 24;289(4):2295-306. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.509216. Epub 2013 Nov 27. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24285541 Free PMC article.
-
Sesamin inhibits bacterial formylpeptide-induced inflammatory responses in a murine air-pouch model and in THP-1 human monocytes.J Nutr. 2010 Feb;140(2):377-81. doi: 10.3945/jn.109.117804. Epub 2009 Dec 23. J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20032476
-
Normal cell surface expression and selective loss of functions resulting from Phe110 to Ser and Cys126 to Trp substitutions in the formyl peptide receptor.Immunol Invest. 2004 May;33(2):193-212. doi: 10.1081/imm-120034234. Immunol Invest. 2004. PMID: 15195697
-
Basic characteristics of the neutrophil receptors that recognize formylated peptides, a danger-associated molecular pattern generated by bacteria and mitochondria.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Aug 15;114:22-39. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.04.014. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27131862 Review.
-
γ-AApeptides as a New Class of Peptidomimetics: Design, Synthesis, and Applications.Curr Top Med Chem. 2021;21(28):2574-2592. doi: 10.2174/1568026621666210727160852. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34315367 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemotactic Ligands that Activate G-Protein-Coupled Formylpeptide Receptors.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 12;20(14):3426. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143426. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31336833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
γ-AApeptides: Design, Structure, and Applications.Acc Chem Res. 2016 Mar 15;49(3):428-41. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00492. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Acc Chem Res. 2016. PMID: 26900964 Free PMC article.
-
The Formyl Peptide Receptors: Diversity of Ligands and Mechanism for Recognition.Molecules. 2017 Mar 13;22(3):455. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030455. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28335409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Development of Antimicrobial Peptidomimetics as Potential Drugs.Molecules. 2017 Aug 29;22(9):1430. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091430. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28850098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
γ-AApeptides as a New Strategy for Therapeutic Development.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(13):2313-2329. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666171107095913. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 29110596 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tosi MF. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005;116:241–249. quiz 250. - PubMed
-
- He R, Tan L, Browning DD, Wang JM, Ye RD. J. Immunol. 2000;165:4598–4605. - PubMed
-
- Mollica A, Paradisi MP, Varani K, Spisani S, Lucente G. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006;14:2253–2265. - PubMed
- Wan HX, Zhou C, Zhang Y, Sun M, Wang X, Yu H, Yang X, Ye RD, Shen JK, Wang MW. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007;74:317–326. - PubMed
- Karlsson J, Fu H, Boulay F, Bylund J, Dahlgren C. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006;71:1488–1496. - PubMed
- Fu H, Karlsson J, Bylund J, Movitz C, Karlsson A, Dahlgren C. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006;79:247–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

