Using cone beam computed tomography to detect the relationship between the periodontal bone loss and mucosal thickening of the maxillary sinus
- PMID: 25225564
- PMCID: PMC4163829
Using cone beam computed tomography to detect the relationship between the periodontal bone loss and mucosal thickening of the maxillary sinus
Abstract
Background: Maxillary sinuses are covered by a 1 mm thick mucous membrane that when this membrane becomes inflamed, the thickness may increase 10-15 times. The common causes of odontogenic sinusitis are dental abscesses and periodontal disease. Computed tomography (CT) is considered the gold standard for sinus diagnosis. Recently, cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) has been introduced for dental and maxillofacial imaging, which has several advantages over traditional CT, including lower radiation dose and chairside process. This study aims to find the association between mucosal thickening (MT) of the sinus and periodontal bone loss (PBL) and pulpoperiapical condition.
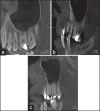
Materials and methods: A total of 180 CBCT images were reviewed. PBL was assessed in six points under each sinus at the mesial and distal sides of the upper second premolar and first and second molars by measuring the distance from the alveolar crest to the point 2 mm under the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ). The MT was assessed at six points in the floor of the sinus precisely over the mentioned points. To assess the possible role of pulpoperiapical condition on the sinus MT, the existing teeth were classified into five groups due to the probable effect of each condition on the pulp and peri-apex. The statistical association between MT of sinus and PBL and pulpoperiapical condition was assessed using SPSS software (SPSS Inc., version 16.0, Chicago, IL, USA) and bivariate correlation and binary linear regression statistical tests (P < 0.05).
Results: MT was observed in 39.4% of patients (mean = 4.68 ± 5.25 mm). PBL was seen in 33% of the patients (mean = 1.87 ± 1.63 mm). Linear regression test showed that there is an association between both PBL and pulpoperiapical condition and MT, but the effect of PBL was about 4 times stronger.
Conclusion: This study showed that MT of the maxillary sinus was common among patients with PBL and MT of the maxillary sinus was significantly associated with PBL.
Keywords: Maxillary sinus; mucosal thickening; periodontal bone loss.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the effect of periapical lesions and other odontogenic conditions on maxillary sinus mucosal thickness characteristics and mucosal appearance: A CBCT study.J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2021 Summer;15(3):163-171. doi: 10.34172/joddd.2021.028. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2021. PMID: 34712406 Free PMC article.
-
Cone beam computed tomographic analysis of maxillary premolars and molars to detect the relationship between periapical and marginal bone loss and mucosal thickness of maxillary sinus.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2015 Sep 1;20(5):e572-9. doi: 10.4317/medoral.20587. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2015. PMID: 26241459 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Posterior Maxillary Teeth on Maxillary Sinus: Insights From Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Dec 29;16(12):e76578. doi: 10.7759/cureus.76578. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39877792 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of CBCT in Evaluating the Health and Pathology of the Maxillary Sinus.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 16;12(11):2819. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12112819. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging technologies for the detection of sinus pathologies of odontogenic origin. A review.Rev Cient Odontol (Lima). 2021 Mar 11;9(1):e049. doi: 10.21142/2523-2754-0901-2021-049. eCollection 2021 Jan-Mar. Rev Cient Odontol (Lima). 2021. PMID: 38464402 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assess the Association Between Periodontitis and Maxillary Sinusitis: A Cross-Sectional Cone-Beam Computerized Tomography (CBCT) Study.Cureus. 2023 Nov 9;15(11):e48587. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48587. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38084169 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the effect of periapical lesions and other odontogenic conditions on maxillary sinus mucosal thickness characteristics and mucosal appearance: A CBCT study.J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2021 Summer;15(3):163-171. doi: 10.34172/joddd.2021.028. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2021. PMID: 34712406 Free PMC article.
-
Median Lingual Foramen, a new midmandibular cephalometric landmark.Orthod Craniofac Res. 2020 Aug;23(3):357-361. doi: 10.1111/ocr.12372. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2020. PMID: 32096318 Free PMC article.
-
Radiological Study of Maxillary Sinus using CBCT: Relationship between Mucosal Thickening and Common Anatomic Variants in Chronic Rhinosinusitis.J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 Nov;10(11):MC07-MC10. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/22365.8931. Epub 2016 Nov 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016. PMID: 28050414 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Relationship of Dimensions of Maxillary Sinus Drainage System with Anatomical Variations and Sinusopathy: Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Findings.Med Princ Pract. 2020;29(4):354-363. doi: 10.1159/000504963. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Med Princ Pract. 2020. PMID: 31760388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soikkonen K, Ainamo A. Radiographic maxillary sinus findings in the elderly. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995;80:487–91. - PubMed
-
- White SC, Pharoah MJ. 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier; 2009. Oral Radiology; pp. 506–12.
-
- Phothikhun S, Suphanantachat S, Chuenchompoonut V, Nisapakultorn K. Cone-beam computed tomographic evidence of the association between periodontal bone loss and mucosal thickening of the maxillary sinus. J Periodontol. 2012;83:557–64. - PubMed
-
- Vallo J, Suominen-Taipale L, Huumonen S, Soikkonen K, Norblad A. Prevalence of mucosal abnormalities of the maxillary sinus and their relationship to dental disease in panoramic radiography: Results from the health 2000 health examination survey. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109:E80–7. - PubMed
-
- Engström H, Chamberlain D, Kiger R, Egelberg J. Radiographic evaluation of the effect of initial periodontal therapy on thickness of the maxillary sinus mucosa. J Periodontol. 1988;59:604–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
