Tumor microenvironmental changes induced by the sulfamate carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitor S4 in a laryngeal tumor model
- PMID: 25225880
- PMCID: PMC4167542
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108068
Tumor microenvironmental changes induced by the sulfamate carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitor S4 in a laryngeal tumor model
Abstract
Background and purpose: Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) plays a pivotal role in pH homeostasis, which is essential for tumor cell survival. We examined the effect of the CAIX inhibitor 4-(3'(3",5"-dimethylphenyl)-ureido)phenyl sulfamate (S4) on the tumor microenvironment in a laryngeal tumor model by analyzing proliferation, apoptosis, necrosis, hypoxia, metabolism and CAIX ectodomain shedding.
Methods: SCCNij202 tumor bearing-mice were treated with S4 for 1, 3 or 5 days. CAIX ectodomain shedding was measured in the serum after therapy. Effects on tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis, necrosis, hypoxia (pimonidazole) and CAIX were investigated with quantitative immunohistochemistry. Metabolic transporters and enzymes were quantified with qPCR.
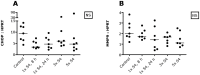
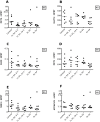
Results: CAIX ectodomain shedding decreased after treatment with S4 (p<0.01). S4 therapy did neither influence tumor cell proliferation nor the amount of apoptosis and necrosis. Hypoxia (pimonidazole) and CAIX expression were also not affected by S4. CHOP and MMP9 mRNA as a reference of intracellular pH did not change upon treatment with S4. Compensatory mechanisms of pH homeostasis at the mRNA level were not observed.
Conclusion: As the clinical and biological meaning of the decrease in CAIX ectodomain shedding after S4 therapy is not clear, studies are required to elucidate whether the CAIX ectodomain has a paracrine or autocrine signaling function in cancer biology. S4 did not influence the amount of proliferation, apoptosis, necrosis and hypoxia. Therefore, it is unlikely that S4 can be used as single agent to influence tumor cell kill and proliferation, and to target primary tumor growth.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Sulfamate Small Molecule CAIX Inhibitor S4 Modulates Doxorubicin Efficacy.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 11;11(8):e0161040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161040. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27513947 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Evaluation of Ureidosulfamate Carbonic Anhydrase IX/XII Inhibitors in the Treatment of Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 2;20(23):6080. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236080. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31810330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulfamate inhibitor S4 influences carbonic anhydrase IX ectodomain shedding in colorectal carcinoma cells.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016 Oct;31(5):779-86. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2015.1069286. Epub 2015 Aug 5. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26244271
-
Evaluation of carbonic anhydrase IX as a therapeutic target for inhibition of breast cancer invasion and metastasis using a series of in vitro breast cancer models.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 22;6(28):24856-70. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4498. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26259239 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX with small organic ligands.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2015 Jun;26:48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25721398 Review.
Cited by
-
The Sulfamate Small Molecule CAIX Inhibitor S4 Modulates Doxorubicin Efficacy.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 11;11(8):e0161040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161040. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27513947 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Evaluation of Ureidosulfamate Carbonic Anhydrase IX/XII Inhibitors in the Treatment of Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 2;20(23):6080. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236080. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31810330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, biological activity and multiscale molecular modeling studies for coumaryl-carboxamide derivatives as selective carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2017 Dec;32(1):1042-1052. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2017.1354857. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28776440 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitor S4 triggers release of DAMPs related to immunogenic cell death in glioma cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jun 29;21(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01180-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37386564 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX and XII isoforms with small molecule inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):1278-1298. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2052868. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35506234 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meijer TW, Kaanders JH, Span PN, Bussink J (2012) Targeting hypoxia, HIF-1, and tumor glucose metabolism to improve radiotherapy efficacy. Clin Cancer Res 18: 5585–5594. - PubMed
-
- Chiche J, Ilc K, Brahimi-Horn MC, Pouyssegur J (2010) Membrane-bound carbonic anhydrases are key pH regulators controlling tumor growth and cell migration. Adv Enzyme Regul 50: 20–33. - PubMed
-
- Neri D, Supuran CT (2011) Interfering with pH regulation in tumours as a therapeutic strategy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10: 767–777. - PubMed
-
- Otero-Rey EM, Somoza-Martin M, Barros-Angueira F, Garcia-Garcia A (2008) Intracellular pH regulation in oral squamous cell carcinoma is mediated by increased V-ATPase activity via over-expression of the ATP6V1C1 gene. Oral Oncol 44: 193–199. - PubMed
-
- Cianchi F, Vinci MC, Supuran CT, Peruzzi B, De Giuli P, et al. (2010) Selective inhibition of carbonic anhydrase IX decreases cell proliferation and induces ceramide-mediated apoptosis in human cancer cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 334: 710–719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

