Alfalfa snakin-1 prevents fungal colonization and probably coevolved with rhizobia
- PMID: 25227589
- PMCID: PMC4177055
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-014-0248-9
Alfalfa snakin-1 prevents fungal colonization and probably coevolved with rhizobia
Abstract
Background: The production of antimicrobial peptides is a common defense strategy of living cells against a wide range of pathogens. Plant snakin peptides inhibit bacterial and fungal growth at extremely low concentrations. However, little is known of their molecular and ecological characteristics, including origin, evolutionary equivalence, specific functions and activity against beneficial microbes. The aim of this study was to identify and characterize snakin-1 from alfalfa (MsSN1).
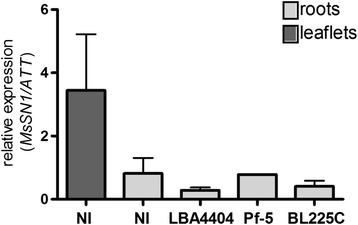
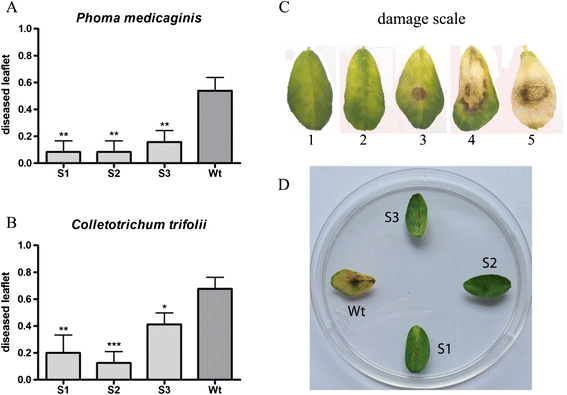
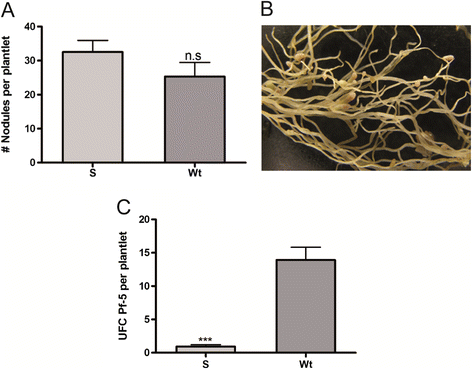
Results: Phylogenetic analysis showed complete congruence between snakin-1 and plant trees. The antimicrobial activity of MsSN1 against bacterial and fungal pathogens of alfalfa was demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. Transgenic alfalfa overexpressing MsSN1 showed increased antimicrobial activity against virulent fungal strains. However, MsSN1 did not affect nitrogen-fixing bacterial strains only when these had an alfalfa origin.
Conclusions: The results reported here suggest that snakin peptides have important and ancestral roles in land plant innate immunity. Our data indicate a coevolutionary process, in which alfalfa exerts a selection pressure for resistance to MsSN1 on rhizobial bacteria. The increased antimicrobial activity against virulent fungal strains without altering the nitrogen-fixing symbiosis observed in MsSN1-overexpressing alfalfa transgenic plants opens the way to the production of effective legume transgenic cultivars for biotic stress resistance.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5 genome-wide mutant screen for resistance to the antimicrobial peptide alfalfa snakin-1.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2015 Jan;362(2):1-6. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnu006. Epub 2014 Dec 4. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25670697
-
Plant transcriptome analysis reveals specific molecular interactions between alfalfa and its rhizobial symbionts below the species level.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Jun 26;20(1):293. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02503-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32590947 Free PMC article.
-
Early recognition in the Rhizobium meliloti-alfalfa symbiosis: root exudate factor stimulates root adsorption of homologous rhizobia.J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3492-9. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3492-3499.1991. J Bacteriol. 1991. PMID: 2045369 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen control of bacterial signal production in Rhizobium meliloti-alfalfa symbiosis.Indian J Exp Biol. 2002 Sep;40(9):981-8. Indian J Exp Biol. 2002. PMID: 12587724 Review.
-
Role of rhizobial biosynthetic pathways of amino acids, nucleotide bases and vitamins in symbiosis.Indian J Exp Biol. 2002 Jul;40(7):755-64. Indian J Exp Biol. 2002. PMID: 12597544 Review.
Cited by
-
Snakins: antimicrobial potential and prospects of genetic engineering for enhanced disease resistance in plants.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Oct;50(10):8683-8690. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08734-5. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37578577 Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Gibberellic Acid-Stimulated Arabidopsis Gene Family in Pineapple (Ananas comosus).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 2;24(23):17063. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317063. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069384 Free PMC article.
-
The dissection of R genes and locus Pc5.1 in Phytophthora capsici infection provides a novel view of disease resistance in peppers.BMC Genomics. 2021 May 21;22(1):372. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07705-z. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34016054 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorus fertilization enhanced overwintering, root system and forage yield of late-seeded alfalfa in sodic soils.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 5;14(1):18090. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67087-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39103386 Free PMC article.
-
Maximizing the expression of transgenic traits into elite alfalfa germplasm using a supertransgene configuration in heterozygous conditions.Theor Appl Genet. 2018 May;131(5):1111-1123. doi: 10.1007/s00122-018-3062-1. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Theor Appl Genet. 2018. PMID: 29397404
References
-
- Volenec JJ, Cunningham SM, Haagenson DM, Berg WK, Joern BC, Wiersma DW. Physiological genetics of alfalfa improvement: past failures, future prospects. Field Crops Res. 2002;75:97–110. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4290(02)00020-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

