Melanization and morphological effects on antifungal susceptibility of Penicillium marneffei
- PMID: 25227777
- PMCID: PMC4194899
- DOI: 10.1007/s10482-014-0270-9
Melanization and morphological effects on antifungal susceptibility of Penicillium marneffei
Abstract
The biosynthesis of melanin has been linked with virulence in diverse pathogenic fungi. Penicillium marneffei, a dimorphic fungus, is capable of melanization in both mycelial and yeast phases, and the pigment may be produced during infection to protect the fungus from the host immune system. To investigate the impact of yeast morphological transformation on antifungal susceptibility, P. marneffei was cultured on various media including minimal medium, 1 % tryptone, brain heart infusion broth, and malt extract broth by using the standardized susceptibility protocol (the M27-A protocol, RPMI medium) for yeasts. We also investigated whether P. marneffei melanization affected its susceptibility to antifungal drugs by adding L-DOPA into culture broths. There were no differences in the minimum inhibitory concentrations of P. marneffei yeast cells previously grown in various culture broths with or without L-DOPA using the M27A protocol (into which no melanin substrate can be added due to a rapid colour change of the RPMI medium to black) for testing amphotericin B, clotrimazole, fluconazole, itraconazole and ketoconazole. However, both melanized and non-melanized P. marneffei displayed increased resistance to antifungal drugs when L-DOPA was added into a selected assay medium, 0.17 % yeast nitrogen base, 2 % glucose, and 1.5 % agar. Hence, active melanin formation appears to protect P. marneffei by enhancing its resistance to antifungal drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


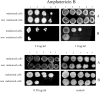

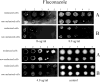
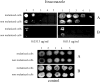
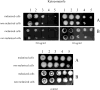
References
-
- Cánovas D, Andrianopoulos A. The Biology of the Thermally Dimorphic Fungal Pathogen Penicillium marneffei. In: Kavanagh K, editor. New Insights in Medical Mycology. Springer; Netherlands: 2007. pp. 213–226.
-
- da Silva MB, Marques AF, Nosanchuk JD, Casadevall A, Travassos LR, Taborda CP. Melanin in the dimorphic fungal pathogen Paracoccidioides brasiliensis: effects on phagocytosis, intracellular resistance and drug susceptibility. Microbes Infect. 2006;8:197–205. - PubMed
-
- Dadachova E, Bryan RA, Howell RC, Schweitzer AD, Aisen P, Nosanchuck JD, Casadevall A. The radioprotective properties of fungal melanin are a function of its chemical composition, stable radical presence and spatial arrangement. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2008;21:192–199. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton AJ, Gómez BL. Melanins in fungal pathogens. J Med Microbiol. 2002;51:189–191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

