Structural basis for the oligomerization of the MADS domain transcription factor SEPALLATA3 in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 25228343
- PMCID: PMC4213154
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.114.127910
Structural basis for the oligomerization of the MADS domain transcription factor SEPALLATA3 in Arabidopsis
Abstract
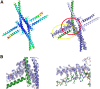
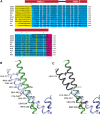
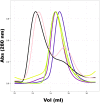
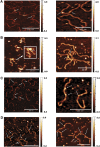
In plants, MADS domain transcription factors act as central regulators of diverse developmental pathways. In Arabidopsis thaliana, one of the most central members of this family is SEPALLATA3 (SEP3), which is involved in many aspects of plant reproduction, including floral meristem and floral organ development. SEP3 has been shown to form homo and heterooligomeric complexes with other MADS domain transcription factors through its intervening (I) and keratin-like (K) domains. SEP3 function depends on its ability to form specific protein-protein complexes; however, the atomic level determinants of oligomerization are poorly understood. Here, we report the 2.5-Å crystal structure of a small portion of the intervening and the complete keratin-like domain of SEP3. The domains form two amphipathic alpha helices separated by a rigid kink, which prevents intramolecular association and presents separate dimerization and tetramerization interfaces comprising predominantly hydrophobic patches. Mutations to the tetramerization interface demonstrate the importance of highly conserved hydrophobic residues for tetramer stability. Atomic force microscopy was used to show SEP3-DNA interactions and the role of oligomerization in DNA binding and conformation. Based on these data, the oligomerization patterns of the larger family of MADS domain transcription factors can be predicted and manipulated based on the primary sequence.
© 2014 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Alvarez-Buylla, E.R., Pelaz, S., Liljegren, S.J., Gold, S.E., Burgeff, C., Ditta, G.S., Ribas de Pouplana, L., Martínez-Castilla, L., Yanofsky, M.F. (2000). An ancestral MADS-box gene duplication occurred before the divergence of plants and animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 5328–5333 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Becker, A., Theissen, G. (2003). The major clades of MADS-box genes and their role in the development and evolution of flowering plants. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 29: 464–489 - PubMed
-
- Becker, A., Winter, K.U., Meyer, B., Saedler, H., Theissen, G. (2000). MADS-Box gene diversity in seed plants 300 million years ago. Mol. Biol. Evol. 17: 1425–1434 - PubMed
-
- Bricogne, G.B.E., Brandl M., Flensburg C., Keller P., Paciorek W., Roversi P., Sharff A., Smart O.S., Vonrhein C., and Womack T.O. (2011). BUSTER version 2.10.0. (Cambridge, UK: Global Phasing Ltd.).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

