EGF up-regulates miR-31 through the C/EBPβ signal cascade in oral carcinoma
- PMID: 25229239
- PMCID: PMC4168139
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108049
EGF up-regulates miR-31 through the C/EBPβ signal cascade in oral carcinoma
Abstract
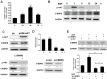
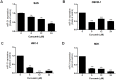
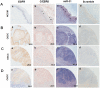
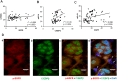
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is one of the most prevalent carcinomas worldwide. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression and modulate physiological or pathological processes including OSCC carcinogenesis. miR-31 has been found to be up-regulated in OSCC and to act as an oncogenic miRNA. However, the molecular mechanism underlying miR-31 up-regulation in OSCC is still obscure. The activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling axis plays key roles in driving oral carcinogenesis. Our screening identified that there is up-regulation of miR-31, miR-181b and miR-222 in OSCC cells following EGF treatment. Subsequent analysis showed that EGF treatment led to AKT activation, which then resulted in miR-31 up-regulation. Moreover, EGF treatment and the AKT activation induced by exogenous expression up-regulated C/EBPβ expression. The miR-31 up-regulation induced by EGF was abrogated by AKT inhibition or by the knockdown of C/EBPβ expression. In OSCC cell subclones stably overexpressing the functional isoform of C/EBPβ, miR-31 expression was up-regulated. Curcumin is a natural ingredient exhibiting anti-cancer potential. It was found that curcumin attenuated AKT activation and the up-regulation of C/EBPβ and miR-31 caused by EGF stimulation in OSCC cells. Lastly, concordance across the expression of EGFR, the expression of C/EBPβ and the expression of miR-31 in OSCC tissues was found. This study describes a novel scenario where the up-regulation of miR-31 expression in OSCC is, at least in part, a consequence of EGFR oncogenic activation. Although the AKT activation and C/EBPβ expression after EGF treatment might not be directly linked, both events are the crucial mediators underlying miR-31 up-regulation in the EGFR signaling axis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Hung PS, Tu HF, Kao SY, Yang CC, Liu CJ, et al. (2014) miR-31 is upregulated in oral premalignant epithelium and contributes to the immortalization of normal oral keratinocytes. Carcinogenesis 35: 1162–1171. - PubMed
-
- Liu CJ, Tsai MM, Hung PS, Kao SY, Liu TY, et al. (2010) miR-31 ablates expression of the HIF regulatory factor FIH to activate the HIF pathway in head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res 70: 1635–1644. - PubMed
-
- Rogers SJ, Harrington KJ, Rhys-Evans P, O-Charoenrat P, Eccles SA (2005) Biological significance of c-erbB family oncogenes in head and neck cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24: 47–69. - PubMed
-
- Tu HF, Lin SC, Chang KW (2013) MicroRNA aberrances in head and neck cancer: pathogenetic and clinical significance. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 21: 104–111. - PubMed
-
- Kalyankrishna S, Grandis JR (2006) Epidermal growth factor receptor biology in head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 24: 2666–2672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

