A novel 3,9-(1,2,3-trioxocine)-type steroid of Rauia nodosa (Rutaceae)
- PMID: 25230120
- PMCID: PMC6271486
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules190914637
A novel 3,9-(1,2,3-trioxocine)-type steroid of Rauia nodosa (Rutaceae)
Abstract
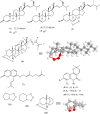
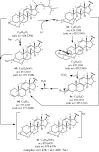
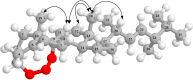
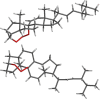
A new natural product, a 3,9-(1,2,3-trioxocine)-type steroid, named rauianodoxy (6), was isolated from Rauia nodosa, together with five steroids: sistostenone (1), stigmastenone (2), sitosterol (3), stigmasterol (4) and ergosterol peroxide (5), one coumarin, O-geranylosthenol (7), and three alkaloids, N-methylflindersine (8), zantobungeanine (9) and veprissine (10). Compounds 5-8 were isolated for the first time in the genus Rauia. These compounds were characterized on the basis of their spectral data, mainly one and two-dimensional NMR, and mass spectra, also involving comparison with the literature data. Theoretical studies at the DFT level reveal structural parameters for the 1,2,3-trioxole bridge compatible with known structures containing a similar group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Barroso G.M., Guimarães E.F., Ichaso C.L.F., Costa C.G., Peixoto A.L., Lima H.C. Sistemática de Angiospermas do Brasil. Universidade Federal de Viçosa; Imprensa Universitária, Viçosa, Brazil: 1986.
-
- Waterman P.G. The chemical systematics of alkaloids: A review emphasizing the contribution of Robert Hegnauer. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1999;27:395–406. doi: 10.1016/S0305-1978(98)00097-0. - DOI
-
- Chase M.W., Morton M.C., Kallunki J.A. Phylogenetic relationships of Rutaceae: A cladistic analysis of the subfamilies using evidence from rbcL e atpB sequence variation. Am. J. Bot. 1999;86:1191–1199. - PubMed
-
- Kallunki J.A., Pirani J.R. Synopses of Angostura Roem. & Schult. and Conchocarpus J.C. Mikan (Rutaceae) Kew Bull. 1998;53:257–334. doi: 10.2307/4114501. - DOI
-
- Albarici T.R., Vieira P.C., Fernandes J.B., Silva M.F.G.F. Cumarinas e alcalóides de Rauia resinosa (Rutaceae) Quim. Nova. 2010;33:2130–2134. doi: 10.1590/S0100-40422010001000024. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

