Smart multi-level tool for remote patient monitoring based on a wireless sensor network and mobile augmented reality
- PMID: 25230306
- PMCID: PMC4208221
- DOI: 10.3390/s140917212
Smart multi-level tool for remote patient monitoring based on a wireless sensor network and mobile augmented reality
Abstract
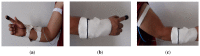
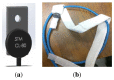
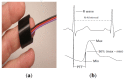
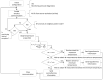
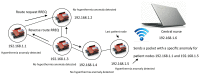
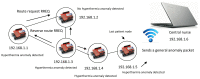
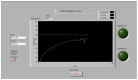
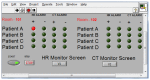
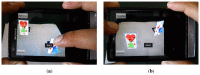
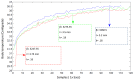
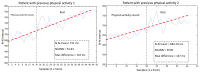
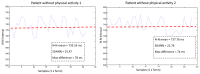
Technological innovations in the field of disease prevention and maintenance of patient health have enabled the evolution of fields such as monitoring systems. One of the main advances is the development of real-time monitors that use intelligent and wireless communication technology. In this paper, a system is presented for the remote monitoring of the body temperature and heart rate of a patient by means of a wireless sensor network (WSN) and mobile augmented reality (MAR). The combination of a WSN and MAR provides a novel alternative to remotely measure body temperature and heart rate in real time during patient care. The system is composed of (1) hardware such as Arduino microcontrollers (in the patient nodes), personal computers (for the nurse server), smartphones (for the mobile nurse monitor and the virtual patient file) and sensors (to measure body temperature and heart rate), (2) a network layer using WiFly technology, and (3) software such as LabView, Android SDK, and DroidAR. The results obtained from tests show that the system can perform effectively within a range of 20 m and requires ten minutes to stabilize the temperature sensor to detect hyperthermia, hypothermia or normal body temperature conditions. Additionally, the heart rate sensor can detect conditions of tachycardia and bradycardia.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Statistics 2010. WHO Press; Geneva, Switzerland: 2010. World Health Organization Health Workforce, Infrastructure and Essential Medicines; pp. 113–124.
-
- Callen J., Hordern A., Gibson K., Li L., Hains I., Westbrook J. Can Technology Change the Work of Nurses? Evaluation of a Drug Monitoring System for Ambulatory Chronic Disease Patients. Int. J. Med. Inf. 2013;82:159–167. - PubMed
-
- Wang D., Wang P. Understanding Security Failures of Two-Factor Authentication Schemes for Real-Time Applications in Hierarchical Wireless Sensor Networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2014;20:1–15.
-
- Kim Y., Lee S. Energy-Efficient Wireless Hospital Sensor Networking for Remote Patient Monitoring. Inf. Sci. 2014;282:332–349.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

