Swept-source OCT angiography of the retinal vasculature using intensity differentiation-based optical microangiography algorithms
- PMID: 25230403
- PMCID: PMC4286454
- DOI: 10.3928/23258160-20140909-08
Swept-source OCT angiography of the retinal vasculature using intensity differentiation-based optical microangiography algorithms
Abstract
Background and objective: To demonstrate the feasibility of using a 1,050-nm swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) system to achieve noninvasive retinal vasculature imaging in human eyes.
Materials and methods: Volumetric data sets were acquired using a 1-µm SS-OCT prototype that operated at a 100-kHz A-line rate. A scanning protocol designed to allow for motion contrast processing, referred to as OCT angiography or optical microangiography (OMAG), was used to scan an approximately 3 × 3–mm area in the central macular region of the retina within approximately 4.5 seconds. An intensity differentiation-based OMAG algorithm was used to extract three-dimensional retinal functional microvasculature information.
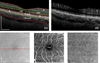
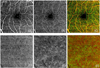
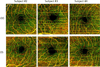
Results: Intensity signal differentiation generated capillary-level resolution en face OMAG images of the retina. The parafoveal capillaries were clearly visible, thereby allowing visualization of the foveal avascular zone in healthy subjects.
Conclusion: The capability of OMAG to produce retinal vascular images was demonstrated using the 1-µm SS-OCT prototype. This technique has potential clinical value for studying retinal vasculature abnormalities.
Figures


References
-
- Bennett TJ, Barry CJ. Ophthalmic imaging today: an ophthalmic photographer's viewpoint - a review. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009;37(1):2–13. - PubMed
-
- Yannuzzi LA, Ober MD, Slakter JS, et al. Ophthalmic fundus imaging: today and beyond. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004;137(3):511–524. - PubMed
-
- Chen ZP, Milner TE, Dave D, Nelson JS. Optical Doppler tomographic imaging of fluid flow velocity in highly scattering media. Opt Lett. 1997;22(1):64–66. - PubMed
-
- White BR, Pierce MC, Nassif N, et al. In vivo dynamic human retinal blood flow imaging using ultra-high-speed spectral domain optical Doppler tomography. Opt Express. 2003;11(25):3490–3497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

