A cross-sectional study on informed choice in the mammography screening programme in Germany (InEMa): a study protocol
- PMID: 25231495
- PMCID: PMC4166244
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006145
A cross-sectional study on informed choice in the mammography screening programme in Germany (InEMa): a study protocol
Abstract
Introduction: Breast cancer is the most prevalent cancer among women. In Germany, women are invited to a population-based mammography screening programme for the first time at the age of 50. Since it is still discussed whether the benefits of mammography screening outweigh its harms, the concept of informed choice has gained importance. The objective of this cross-sectional study is to assess the proportion of informed choices in the mammography screening programme. A special focus is on the examination of the impact of Turkish migration background and educational level on informed choices.
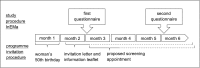
Methods and analysis: The proportion of informed choices is evaluated in a cross-sectional study with 3-month follow-up for behavioural implementation of the screening intention. A randomly selected sample of 17,000 women aged 50 years living in Westphalia-Lippe, a region in the Federal State of North-Rhine Westphalia, is invited to participate in this study. To reach adequate numbers of Turkish women, all possibly Turkish women in the sample are identified through a name algorithm and contacted. The sample is drawn from women registered in the study area for which the registration offices consented to supply data for the study (88% of all towns/cities in the study region). Women identified through the Turkish name algorithm received all materials in German and Turkish. The primary outcome is informed choice. Data are collected on informed choice components (knowledge, attitude, decision/implementation) as well as on its possible determinants (eg, health behaviour, perceived behavioural control, subjective norms, invitation status, migration background and other demographic variables). Data are collected before the screening appointment and at 3 months follow-up.
Ethics and dissemination: The study was approved by the ethical committee of the Medical Faculty of Muenster University. Results will be published in a relevant scientific journal and communicated to respondents and relevant institutions.
Keywords: informed choice; mammography screening; migrants; participation; social determinants.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does a decision aid improve informed choice in mammography screening? Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.BMC Womens Health. 2015 Jul 22;15:53. doi: 10.1186/s12905-015-0210-5. BMC Womens Health. 2015. PMID: 26198675 Free PMC article.
-
Informed Choice in the German Mammography Screening Program by Education and Migrant Status: Survey among First-Time Invitees.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 3;10(11):e0142316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142316. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26529513 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Determinants of mammography screening participation among Turkish immigrant women in Germany--a qualitative study reflecting key informants' and women's perspectives.Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2016 Jan;25(1):38-48. doi: 10.1111/ecc.12334. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2016. PMID: 26052964
-
[Mammography and cervical cancer screening--a systematic review about women's knowledge, attitudes and participation in Germany].Gesundheitswesen. 2012 Nov;74(11):722-35. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1286271. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Gesundheitswesen. 2012. PMID: 22012563 German.
-
[Time trend in programme sensitivity within the German mammography screening programme in North Rhine-Westphalia and Lower Saxony].Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2018 Dec;61(12):1517-1527. doi: 10.1007/s00103-018-2843-7. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2018. PMID: 30421287 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Comparing adaptive and fixed bandwidth-based kernel density estimates in spatial cancer epidemiology.Int J Health Geogr. 2015 Mar 31;14:15. doi: 10.1186/s12942-015-0005-9. Int J Health Geogr. 2015. PMID: 25889018 Free PMC article.
-
Does a decision aid improve informed choice in mammography screening? Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.BMC Womens Health. 2015 Jul 22;15:53. doi: 10.1186/s12905-015-0210-5. BMC Womens Health. 2015. PMID: 26198675 Free PMC article.
-
Do Women With High eHealth Literacy Profit More From a Decision Aid on Mammography Screening? Testing the Moderation Effect of the eHEALS in a Randomized Controlled Trial.Front Public Health. 2019 Mar 12;7:46. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2019.00046. eCollection 2019. Front Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30931291 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer incidence and mammography screening among resettlers in Germany.BMC Public Health. 2020 Mar 30;20(1):417. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-08534-7. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32228537 Free PMC article.
-
Informed Choice in the German Mammography Screening Program by Education and Migrant Status: Survey among First-Time Invitees.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 3;10(11):e0142316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142316. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26529513 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- von Karsa L, Anttila A, Ronco G, et al. Cancer screening in the European Union: Report on the implementation of the Council Recommendation on cancer screening International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2008. http://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_determinants/genetics/documents/cancer_scr... (accessed 17 Jul 2014)
-
- Robert Koch-Institut und die Gesellschaft der epidemiologischen Krebsregister in Deutschland e.V. Krebs in Deutschland 2009/2010, 9th edn. Berlin, 2013
-
- Kooperationsgemeinschaft Mammographie. Evaluationsbericht 2005–2007—Ergebnisse des Mammographie-Screening-Programms in Deutschland, 2009. http://www.mammo-programm.de/cms_upload/datenpool/evaluationsbericht05–0... (accessed 8 Feb 2013)
-
- Kooperationsgemeinschaft Mammographie. Evaluationsbericht 2008–2009—Ergebnisse des Mammographie-Screening-Programms in Deutschland, 2012. http://www.mammo-programm.de/cms_upload/datenpool/evaluationsbericht_200... (accessed 8 Feb 2013)
-
- Perry N, Broeders M, de Wolf C, et al. European guidelines for quality assurance in breast cancer screening and diagnosis. 4th edn Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, 2006
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical