A comparative study of Widal test with blood culture in the diagnosis of typhoid fever in febrile patients
- PMID: 25231649
- PMCID: PMC4177418
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-653
A comparative study of Widal test with blood culture in the diagnosis of typhoid fever in febrile patients
Abstract
Background: Typhoid fever is a major health problem in developing countries and its diagnosis on clinical ground is difficult. Diagnosis in developing countries including Ethiopia is mostly done by Widal test. However, the value of the test has been debated. Hence, evaluating the result of this test is necessary for correct interpretation of the result. The main aim of this study was to compare the result of Widal test and blood culture in the diagnosis of typhoid fever in febrile patients.
Methods: Blood samples were collected from 270 febrile patients with symptoms clinically similar to typhoid fever and visiting St. Paul's General Specialized Hospitals from mid December 2010 to March 2011. Blood culture was used to isolate S.typhi and S.paratyphi. Slide agglutination test and tube agglutination tests were used for the determination of antibody titer. An antibody titer of ≥1:80 for anti TO and ≥1:160 for anti TH were taken as a cut of value to indicate recent infection of typhoid fever.
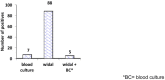
Results: One hundred and eighty six (68.9%) participants were females and eighty four (31.1%) were males. 7 (2.6%) cases of S. typhi and 4 (1.5%) cases of S. paratyphi were identified with the total prevalence of typhoid fever 4.1%. The total number of patients who have indicative of recent infection by either of O and H antigens Widal test is 88 (32.6%). The sensitivity, specificity, Positive predictive Value and Negative predictive Value of Widal test were 71.4%, 68.44%, 5.7% and 98.9% respectively.
Conclusions: Widal test has a low sensitivity, specificity and PPV, but it has good NPV which indicates that negative Widal test result have a good indication for the absence of the disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Typhoid fever among febrile Nigerian patients: Prevalence, diagnostic performance of the Widal test and antibiotic multi-drug resistance.Malawi Med J. 2019 Sep;31(3):184-192. doi: 10.4314/mmj.v31i3.4. Malawi Med J. 2019. PMID: 31839887 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Typhoid Fever and Associated Prevailing Drug Resistance in Northern Ethiopia.Int J Infect Dis. 2015 Jun;35:96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2015.04.014. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Int J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25931197
-
The dilemma of widal test - which brand to use? a study of four different widal brands: a cross sectional comparative study.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2011 Feb 8;10:7. doi: 10.1186/1476-0711-10-7. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2011. PMID: 21303511 Free PMC article.
-
Typhoid fever: misuse of Widal test in Libya.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2014 Jun 11;8(6):680-7. doi: 10.3855/jidc.3700. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2014. PMID: 24916864 Review.
-
Comparative accuracy of typhoid diagnostic tools: A Bayesian latent-class network analysis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 May 8;13(5):e0007303. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007303. eCollection 2019 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31067228 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of classic signs as diagnostic predictors for enteric fever among returned travellers: Relative bradycardia and eosinopenia.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 23;12(6):e0179814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179814. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28644847 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary Anti-50 kDa Antibodies as a Useful Biomarker for Diagnosis of Typhoid Fever.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Jun;11(6):DC10-DC13. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/21928.10055. Epub 2017 Jun 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017. PMID: 28764158 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi infection, its associated factors and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns among febrile patients at Adare general hospital, Hawassa, southern Ethiopia.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Jan 7;21(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05726-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33413186 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid stool antigenic test for typhoid fever among suspected cases, Northeast, Ethiopia.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 12;13(1):649. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27909-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36635427 Free PMC article.
-
Typhoid fever among febrile Nigerian patients: Prevalence, diagnostic performance of the Widal test and antibiotic multi-drug resistance.Malawi Med J. 2019 Sep;31(3):184-192. doi: 10.4314/mmj.v31i3.4. Malawi Med J. 2019. PMID: 31839887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gopalakrishnan V, Sekhar WY, Soo EH, Vinsent RA, Devi S. Typhoid fever in Kuala Lumpur and a comparative evaluation of two commercial diagnostic kits for the detection of antibodies to salmonella typhi. Singapore Med J. 2002;43(7):354–358. - PubMed
-
- Onyekewere CA. Typhoid fever: misdiagnosis or over diagnosis. Niger Med Pract. 2007;51(4):76–79.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources