Assessment of the prophylactic role of aspirin and/or clopidogrel on experimentally induced acute myocardial infarction in hypercholesterolemic rats
- PMID: 25231707
- PMCID: PMC4269823
- DOI: 10.1007/s40268-014-0059-3
Assessment of the prophylactic role of aspirin and/or clopidogrel on experimentally induced acute myocardial infarction in hypercholesterolemic rats
Abstract
Introduction: Hyperlipidemia is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as acute infarction. Inflammation and platelet activation are critical phenomena in acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
Aim: The aim of the study was to assess potential protective effects of aspirin and/or clopidogrel on AMI in hypercholesterolemic rats.
Methods: Forty adult male Wistar rats were divided into five groups (eight rats in each). Group I included normal healthy rats. The other 32 rats were subjected to induction of hypercholesterolemia by high-fat diet for 3 weeks, followed by induction of AMI by subcutaneous injections of isoproterenol (85 mg/kg/day, for 2 days). Rats were divided into the following groups: group II, rats with induced hypercholesterolemia and AMI; group III, hypercholesterolemic rats that received aspirin 30 mg/kg/day orally for 7 days before induction of AMI; group IV, hypercholesterolemic rats that received clopidogrel 10 mg/kg/day orally for 7 days before induction of AMI; and group V, hypercholesterolemic rats treated with both aspirin and clopidogrel in the same doses for 7 days before induction of AMI. Serum levels of pentraxin 3 (PTX3), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), total cholesterol and triglycerides were estimated in all rats.
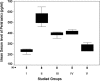
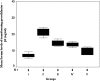
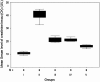
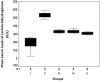
Results: Isoproterenol-induced AMI in hypercholesterolemic rats was associated with an increase in serum levels of PTX3, TGF-β1, CK and LDH. Aspirin and/or clopidogrel pretreatment for 1 week led to a reduction of their levels as compared with non-treated rats. However, the reduction caused by combination of aspirin and clopidogrel was more than that caused by each drug separately.
Conclusion: Combination of aspirin and clopidogrel could be a therapeutic option for hypercholesterolemic patients to attenuate the complex vascular inflammatory process which is a key step in the setting of AMI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clopidogrel Prophylaxis Abates Myocardial Ischemic Injury and Inhibits the Hyperlipidemia-Inflammation Loop in Hypercholestrolemic Mice.Arch Med Res. 2020 Aug;51(6):515-523. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.05.003. Epub 2020 May 31. Arch Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32487324
-
Clopidogrel or prasugrel reduces mortality and lessens cardiovascular damage from acute myocardial infarction in hypercholesterolemic male rats.Life Sci. 2020 Apr 15;247:117429. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117429. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32061670
-
Adding cilostazol to dual antiplatelet therapy achieves greater platelet inhibition than high maintenance dose clopidogrel in patients with acute myocardial infarction: Results of the adjunctive cilostazol versus high maintenance dose clopidogrel in patients with AMI (ACCEL-AMI) study.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2010 Feb 1;3(1):17-26. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.109.880179. Epub 2010 Jan 26. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2010. PMID: 20118150 Clinical Trial.
-
Aspirin, ticlopidine, and clopidogrel in acute coronary syndromes: underused treatments could save thousands of lives.Cleve Clin J Med. 1999 Nov-Dec;66(10):615-8, 621-4, 627-8. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.66.10.615. Cleve Clin J Med. 1999. PMID: 10598366 Review.
-
Role of antiplatelet drugs in the prevention of cardiovascular events.Thromb Res. 2003 Jun 15;110(5-6):355-9. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2003.08.003. Thromb Res. 2003. PMID: 14592562 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypolipidemic, antioxidant and anti-atherosclerogenic effect of aqueous extract leaves of Cassia. occidentalis Linn (Caesalpiniaceae) in diet-induced hypercholesterolemic rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jan 25;17(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1566-x. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28122565 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-induced mitochondrial toxicity: Risks of developing glucose handling impairments.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 13;14:1123928. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1123928. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36860368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Multiple Pharmacologic Functions and Mechanisms of Action of Guizhi Fuling Formulation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Apr 29;2022:6813421. doi: 10.1155/2022/6813421. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35529925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic anti-atherosclerotic role of combined treatment of omega-3 and co-enzyme Q10 in hypercholesterolemia-induced obese rats.Heliyon. 2020 Apr 1;6(4):e03659. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03659. eCollection 2020 Apr. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32258512 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of kampo formulas on the progression of hypercholesterolemia and Fatty liver induced by high-cholesterol diet in rats.Yonago Acta Med. 2014 Dec;57(4):147-58. Epub 2014 Dec 26. Yonago Acta Med. 2014. PMID: 25901102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roffi M, Brindle M, Robbins M, Mukherjee D. Current perspectives on coronary revascularization in diabetic patients. Indian Heart J. 2007;59:124–136. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

