Interplay between sumoylation and phosphorylation for protection against α-synuclein inclusions
- PMID: 25231978
- PMCID: PMC4223324
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.559237
Interplay between sumoylation and phosphorylation for protection against α-synuclein inclusions
Abstract
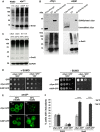
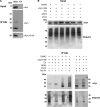
Parkinson disease is associated with the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons from the substantia nigra. The pathological hallmark of the disease is the accumulation of intracytoplasmic inclusions known as Lewy bodies that consist mainly of post-translationally modified forms of α-synuclein. Whereas phosphorylation is one of the major modifications of α-synuclein in Lewy bodies, sumoylation has recently been described. The interplay between α-synuclein phosphorylation and sumoylation is poorly understood. Here, we examined the interplay between these modifications as well as their impact on cell growth and inclusion formation in yeast. We found that α-synuclein is sumoylated in vivo at the same sites in yeast as in human cells. Impaired sumoylation resulted in reduced yeast growth combined with an increased number of cells with inclusions, suggesting that this modification plays a protective role. In addition, inhibition of sumoylation prevented autophagy-mediated aggregate clearance. A defect in α-synuclein sumoylation could be suppressed by serine 129 phosphorylation by the human G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (GRK5) in yeast. Phosphorylation reduced foci formation, alleviated yeast growth inhibition, and partially rescued autophagic α-synuclein degradation along with the promotion of proteasomal degradation, resulting in aggregate clearance in the absence of a small ubiquitin-like modifier. These findings suggest a complex interplay between sumoylation and phosphorylation in α-synuclein aggregate clearance, which may open new horizons for the development of therapeutic strategies for Parkinson disease.
Keywords: Autophagy; Post-translational Modification; Proteasome; Yeast; α-Synuclein.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Posttranslational Modifications and Clearing of α-Synuclein Aggregates in Yeast.Biomolecules. 2015 Apr 23;5(2):617-34. doi: 10.3390/biom5020617. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 25915624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aggregate clearance of α-synuclein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae depends more on autophagosome and vacuole function than on the proteasome.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 10;287(33):27567-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.361865. Epub 2012 Jun 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22722939 Free PMC article.
-
C-Terminal Tyrosine Residue Modifications Modulate the Protective Phosphorylation of Serine 129 of α-Synuclein in a Yeast Model of Parkinson's Disease.PLoS Genet. 2016 Jun 24;12(6):e1006098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006098. eCollection 2016 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27341336 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasome inhibition induces α-synuclein SUMOylation and aggregate formation.J Neurol Sci. 2011 Aug 15;307(1-2):157-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2011.04.015. Epub 2011 Jun 8. J Neurol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21641618 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of alpha-synuclein post-translational modifications on metal binding.J Neurochem. 2019 Sep;150(5):507-521. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14721. Epub 2019 Jul 9. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 31099098 Review.
Cited by
-
In silico comparative analysis of LRRK2 interactomes from brain, kidney and lung.Brain Res. 2021 Aug 15;1765:147503. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147503. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33915162 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranslational Modifications and Clearing of α-Synuclein Aggregates in Yeast.Biomolecules. 2015 Apr 23;5(2):617-34. doi: 10.3390/biom5020617. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 25915624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Search of Effective Treatments Targeting α-Synuclein Toxicity in Synucleinopathies: Pros and Cons.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 4;8:559791. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.559791. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33015057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular models of alpha-synuclein toxicity and aggregation.J Neurochem. 2019 Sep;150(5):566-576. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14806. Epub 2019 Jul 30. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 31265132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SUMO1-conjugation is altered during normal aging but not by increased amyloid burden.Aging Cell. 2018 Aug;17(4):e12760. doi: 10.1111/acel.12760. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Aging Cell. 2018. PMID: 29633471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Obeso J. A., Rodriguez-Oroz M. C., Goetz C. G., Marin C., Kordower J. H., Rodriguez M., Hirsch E. C., Farrer M., Schapira A. H., Halliday G. (2010) Missing pieces in the Parkinson's disease puzzle. Nat. Med. 16, 653–661 - PubMed
-
- Galvin J. E., Lee V. M., Trojanowski J. Q. (2001) Synucleinopathies: clinical and pathological implications. Arch. Neurol. 58, 186–190 - PubMed
-
- Forno L. S., DeLanney L. E., Irwin I., Langston J. W. (1996) Electron microscopy of Lewy bodies in the amygdala-parahippocampal region. Comparison with inclusion bodies in the MPTP-treated squirrel monkey. Adv. Neurol. 69, 217–228 - PubMed
-
- Spillantini M. G., Schmidt M. L., Lee V. M., Trojanowski J. Q., Jakes R., Goedert M. (1997) α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388, 839–840 - PubMed
-
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Lavedan C., Leroy E., Ide S. E., Dehejia A., Dutra A., Pike B., Root H., Rubenstein J., Boyer R., Stenroos E. S., Chandrasekharappa S., Athanassiadou A., Papapetropoulos T., Johnson W. G., Lazzarini A. M., Duvoisin R. C., Di Iorio G., Golbe L. I., Nussbaum R. L. (1997) Mutation in the α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science 276, 2045–2047 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

