Regulation of synaptic extracellular matrix composition is critical for proper synapse morphology
- PMID: 25232106
- PMCID: PMC4166155
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1183-14.2014
Regulation of synaptic extracellular matrix composition is critical for proper synapse morphology
Abstract
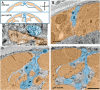
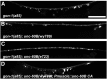
Synapses are surrounded by a layer of extracellular matrix (ECM), which is instrumental for their development and maintenance. ECM composition is dynamically controlled by proteases, but how the precise composition of the ECM affects synaptic morphology is largely unknown. Through an unbiased forward genetic screen, we found that Caenorhabditis elegans gon-1, a conserved extracellular ADAMTS protease, is required for maintaining proper synaptic morphology at the neuromuscular junction. In gon-1 mutants, once synapse formation is complete, motor neuron presynaptic varicosities develop into large bulbous protrusions that contain synaptic vesicles and active zone proteins. A concomitant overgrowth of postsynaptic muscle membrane is found in close apposition to presynaptic axonal protrusions. Mutations in the muscle-specific, actin-severing protein cofilin (unc-60) suppress the axon phenotype, suggesting that muscle outgrowth is necessary for presynaptic protrusions. gon-1 mutants can also be suppressed by loss of the ECM components collagen IV (EMB-9) and fibulin (FBL-1). We propose that GON-1 regulates a developmental switch out of an initial "pro-growth" phase during which muscle arms grow out and form synapses with motor neuron axons. We postulate that this switch involves degradation or reorganization of collagen IV (EMB-9), whereas FBL-1 opposes GON-1 by stabilizing EMB-9. Our results describe a mechanism for regulating synaptic ECM composition and reveal the importance of precise ECM composition for neuronal morphology and synapse integrity.
Keywords: extracellular matrix; metalloproteinase; synapse.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/3412678-12$15.00/0.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Tissue architecture in the Caenorhabditis elegans gonad depends on interactions among fibulin-1, type IV collagen and the ADAMTS extracellular protease.Genetics. 2012 Apr;190(4):1379-88. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.133173. Epub 2012 Jan 31. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22298704 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic interactions among ADAMTS metalloproteases and basement membrane molecules in cell migration in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 2;15(12):e0240571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240571. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33264296 Free PMC article.
-
Perlecan antagonizes collagen IV and ADAMTS9/GON-1 in restricting the growth of presynaptic boutons.J Neurosci. 2014 Jul 30;34(31):10311-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5128-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25080592 Free PMC article.
-
MMP-mediated modulation of ECM environment during axonal growth and NMJ development.Neurosci Lett. 2020 Apr 17;724:134822. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.134822. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Neurosci Lett. 2020. PMID: 32061716 Review.
-
Collagen XIII and Other ECM Components in the Assembly and Disease of the Neuromuscular Junction.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2020 Jun;303(6):1653-1663. doi: 10.1002/ar.24092. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 30768864 Review.
Cited by
-
Dopamine Receptor Activation Modulates the Integrity of the Perisynaptic Extracellular Matrix at Excitatory Synapses.Cells. 2020 Jan 21;9(2):260. doi: 10.3390/cells9020260. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31972963 Free PMC article.
-
Proteins and Transcriptional Dysregulation of the Brain Extracellular Matrix in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 18;24(8):7435. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087435. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108598 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-brain barrier dysfunction as a potential therapeutic target for neurodegenerative disorders.Arch Pharm Res. 2021 May;44(5):487-498. doi: 10.1007/s12272-021-01332-8. Epub 2021 May 24. Arch Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 34028650 Review.
-
Post-synaptic specialization of the neuromuscular junction: junctional folds formation, function, and disorders.Cell Biosci. 2022 Jun 19;12(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00829-z. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35718785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basement membrane patterning by spatial deployment of a secretion-regulating protease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 10:2024.07.06.602330. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.06.602330. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 May 20;122(20):e2412161122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2412161122. PMID: 39026720 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
