Broadly neutralizing antibodies abrogate established hepatitis C virus infection
- PMID: 25232181
- PMCID: PMC4312107
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3009512
Broadly neutralizing antibodies abrogate established hepatitis C virus infection
Abstract
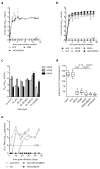
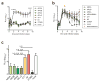
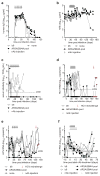
In most exposed individuals, hepatitis C virus (HCV) establishes a chronic infection; this long-term infection in turn contributes to the development of liver diseases such as cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. The role of antibodies directed against HCV in disease progression is poorly understood. Neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) can prevent HCV infection in vitro and in animal models. However, the effects of nAbs on an established HCV infection are unclear. We demonstrate that three broadly nAbs-AR3A, AR3B, and AR4A-delivered with adeno-associated viral vectors can confer protection against viral challenge in humanized mice. Furthermore, we provide evidence that nAbs can abrogate an ongoing HCV infection in primary hepatocyte cultures and in a human liver chimeric mouse model. These results showcase a therapeutic approach to interfere with HCV infection by exploiting a previously unappreciated need for HCV to continuously infect new hepatocytes to sustain a chronic infection.
Copyright © 2014, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Jesudian AB, de Jong YP, Jacobson IM. Emerging therapeutic targets for hepatitis C virus infection. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology. 2013;11:612–619. e611. - PubMed
-
- Beld M, Penning M, van Putten M, van den Hoek A, Damen M, Klein MR, Goudsmit J. Low levels of hepatitis C virus RNA in serum, plasma, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of injecting drug users during long antibody-undetectable periods before seroconversion. Blood. 1999;94:1183–1191. - PubMed
-
- Logvinoff C, Major ME, Oldach D, Heyward S, Talal A, Balfe P, Feinstone SM, Alter H, Rice CM, McKeating JA. Neutralizing antibody response during acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101:10149–10154. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Netski DM, Mosbruger T, Depla E, Maertens G, Ray SC, Hamilton RG, Roundtree S, Thomas DL, McKeating J, Cox A. Humoral immune response in acute hepatitis C virus infection. Clinical infectious diseases. 2005;41:667–675. - PubMed
-
- Pestka JM, Zeisel MB, Blaser E, Schurmann P, Bartosch B, Cosset FL, Patel AH, Meisel H, Baumert J, Viazov S, Rispeter K, Blum HE, Roggendorf M, Baumert TF. Rapid induction of virus-neutralizing antibodies and viral clearance in a single-source outbreak of hepatitis C. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007;104:6025–6030. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI072613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI071084/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI072613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI079031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI099284/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI079031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI10730101/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08DK090576/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA057973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK090576/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI071084/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30CA016087-32/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K22 AI102769/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI099284/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI107301/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA057973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

