A retrospective analysis of plasma D-dimer dynamic variation in terminal stage cancer patients: implications for disease progression
- PMID: 25232445
- PMCID: PMC4161605
A retrospective analysis of plasma D-dimer dynamic variation in terminal stage cancer patients: implications for disease progression
Abstract
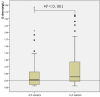
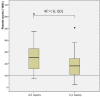
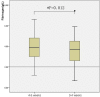
Elevated D-dimer is frequently found among cancer patients especially for advanced stage patients. Activation of the coagulation system and the fibrinolytic cascade are supposed to be associated with higher risk of invasion, metastases and worse outcome. The purpose of this study is to investigate the dynamic variation of plasma D-dimer and its relationship with other markers of the coagulation system including platelet counts, fibrinogen levels, prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) and thrombin time (TT) in terminal stage cancer patients. We designed a self-controlled study to compare plasma D-dimer dynamic variation from 0-4 weeks to 4-8 weeks before patients' death. The plasma D-dimer levels pointed an elevated tendency and revealed statistically significant difference as patients gradually near death. Prolonged PT, APTT and TT were found. D-dimer levels were positively correlated with PT, APTT and TT but showed negative correlation with platelet counts and fibrinogen levels. Plasma D-dimer levels gradually increased as terminal stage cancer patients approaching to death. Increasing D-dimer levels may predict worse outcome.
Keywords: D-dimer; cancer; disease progression; dynamic variation; terminal stage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Analysis of the factors associated with abnormal coagulation and prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014 Nov;17(11):789-96. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2014.11.04. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25404269 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Noninvasive evaluation of ovarian endometriosis: a single-center experience.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Apr;10(4):4728-4735. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-481. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 33966422
-
The prognostic value of D-dimer in lung cancer.Clin Respir J. 2015 Jul;9(3):305-13. doi: 10.1111/crj.12144. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Clin Respir J. 2015. PMID: 24720709
-
Clinical and prognostic significance of coagulation assays in melanoma.Melanoma Res. 2012 Oct;22(5):368-75. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0b013e328357be7c. Melanoma Res. 2012. PMID: 22889867
-
[Coagulopathy correlates with outcomes in patients with community- acquired pneumonia].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2014 Jun;37(6):406-10. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25200038 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Preoperative D-dimer level is an independent prognostic factor for non-small cell lung cancer after surgical resection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Aug;7(16):366. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.05.35. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31555680 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of plasma D-dimer in ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jun;96(25):e7062. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007062. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28640083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High pretreatment plasma D-dimer levels predict poor prognosis in gastrointestinal cancers: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jul;98(29):e16520. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016520. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31335729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sood SL. Cancer-associated thrombosis. Curr Opin Hematol. 2009;16:378–385. - PubMed
-
- Sumney M, Whiteman K, editors. D-dimer: Past, present, and future. CE Connection available at: http://www.nursingcenter.com. Accessed Oct. 10, 2010.
-
- Lee AY. Thrombosis and cancer: the role of screening for occult cancer and recognizing the underlying biological mechanisms. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2006;6:438–43. - PubMed
-
- Amirkhosravi A, Meyer T, Amaya M, Davila M, Mousa SA, Robson T, Francis JL. The role of tissue factor pathway inhibitor in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2007 Oct;33:643–52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
