EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC patients: mechanisms and strategies
- PMID: 25232485
- PMCID: PMC4163608
EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC patients: mechanisms and strategies
Abstract
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a kind of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) that plays a critical role in the initiation and development of malignant tumors via modulating downstream signaling pathways. In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the activating mutations located in the tyrosine kinase domains of EGFR have been demonstrated in multiple researches as the "Achilles' heel" of this deadly disease since they could be well-targeted by epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs). However, it's still too early to celebrate since the first-generation EGFR-TKIs such as gefitinib and erlotinib have only achieved limited clinical benefits and acquired resistance to this kind of drugs occurred inevitably in almost all the NSCLC patients. In order to make the most of EGFR-TKIs and develop more effective regimens for the NSCLC patients, researchers majoring in different aspects start a battle against EGFR-TKI resistance. Challenging as it is, we still progress stably and step firmly toward the final victory. This review will summarize the major mechanisms of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs, and then discuss the development of rationally designed molecular target drugs in accordance with each mechanism, in the hope of shedding light on the great achievements we have obtained and tough obstacles we have to overcome in the battle against this deadly disease.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer; drug resistance; epithelial growth factor receptor; molecular targeted therapy; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
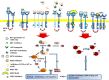
Figures

References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Klastersky J, Awada A. Milestones in the use of chemotherapy for the management of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2012;81:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Hynes NE, Lane HA. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:341–354. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
