Expression of peroxiredoxin 1 and 4 promotes human lung cancer malignancy
- PMID: 25232487
- PMCID: PMC4163610
Expression of peroxiredoxin 1 and 4 promotes human lung cancer malignancy
Abstract
Members of the Peroxiredoxin (Prx) family are major cellular antioxidants that scavenge hydrogen peroxide and play essential roles in oxidative stress and cell signaling. 2-Cys Prxs, including Prx1, 2, 3 and 4, have been indicated in multiple oncogenic signaling pathways and thus may contribute to various processes of cancer development. The significance of 2-Cys Prxs in lung cancer development and their biological function in signal transduction have not been fully investigated. In this study we analyzed the expression of 2-Cys Prxs in lung cancer, and examined their levels of expression in a variety of cell lines established from human lung normal or cancer tissues. We found that 2-Cys Prxs, in particular, Prx1 and Prx4, were preferentially expressed in cell lines derived from human lung cancer. Through isoform specific knockdown of individual Prx, we demonstrated that Prx1 and Prx4 (but not Prx3) were required for human lung cancer A549 cells to form soft agar colony and to invade through matrigel in culture. Knockdown of Prx1 or Prx4 significantly reduced the activation of c-Jun and repressed the AP-1 mediated promoter activity. In mouse xenograft models, knockdown of Prx4 in A549 cells reduced subcutaneous tumor growth and blocked metastasis formation initiated through tail vein injection. Moreover, overexpression of Prx1 or Prx4 further enhanced the malignancy of A549 cells both in culture and in mouse xenografts in vivo. These data provide an in-depth understanding of the contribution of Prx1 and Prx4 to lung cancer development and are of importance for future development of therapeutic methods that targeting 2-Cys Prxs.
Keywords: Peroxiredoxin; cell signaling; lung cancer; tumor invasion and metastasis.
Figures
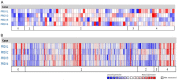


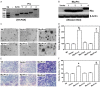
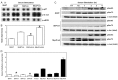

Similar articles
-
Characterization of 2-Cys peroxiredoxin 3 and 4 in common carp and the immune response against bacterial infection.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Mar;217:60-69. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2017.12.012. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29277606
-
Differences in Proinflammatory Property of Six Subtypes of Peroxiredoxins and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Ligustilide in Macrophages.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 7;11(10):e0164586. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164586. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27716839 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of six peroxiredoxin transcripts from mud crab Scylla paramamosain: The first evidence of peroxiredoxin gene family in crustacean and their expression profiles under biotic and abiotic stresses.Mol Immunol. 2018 Jan;93:223-235. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.11.029. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29220745
-
Role of Cytosolic 2-Cys Prx1 and Prx2 in Redox Signaling.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Jun 10;8(6):169. doi: 10.3390/antiox8060169. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31185618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological Significance of Plant Peroxiredoxins and the Structure-Related and Multifunctional Biochemistry of Peroxiredoxin 1.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Mar 1;28(7):625-639. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7400. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 29113450 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential Roles of Peroxiredoxin IV in Inflammation and Cancer.Molecules. 2022 Oct 2;27(19):6513. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196513. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Suppression Taurine on Relocation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Mankind Lung Cancer Cells.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Apr 14;2021:6656080. doi: 10.1155/2021/6656080. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 4;2023:9893582. doi: 10.1155/2023/9893582. PMID: 33936579 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Total synthesis of griseusins and elucidation of the griseusin mechanism of action.Chem Sci. 2019 Jun 27;10(32):7641-7648. doi: 10.1039/c9sc02289a. eCollection 2019 Aug 28. Chem Sci. 2019. PMID: 31583069 Free PMC article.
-
Frenolicin B Targets Peroxiredoxin 1 and Glutaredoxin 3 to Trigger ROS/4E-BP1-Mediated Antitumor Effects.Cell Chem Biol. 2019 Mar 21;26(3):366-377.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2018.11.013. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Cell Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 30661989 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxiredoxins and Beyond; Redox Systems Regulating Lung Physiology and Disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019 Nov 10;31(14):1070-1091. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7752. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019. PMID: 30799628 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rhee SG, Chae HZ, Kim K. Peroxiredoxins: a historical overview and speculative preview of novel mechanisms and emerging concepts in cell signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005;38:1543–1552. - PubMed
-
- Okado-Matsumoto A, Matsumoto A, Fujii J, Taniguchi N. Peroxiredoxin IV is a secretable protein with heparin-binding properties under reduced conditions. J Biochem. 2000;127:493–501. - PubMed
-
- Prosperi MT, Ferbus D, Karczinski I, Goubin G. A human cDNA corresponding to a gene overexpressed during cell proliferation encodes a product sharing homology with amoebic and bacterial proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:11050–11056. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
