Improved cerebral time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography at 7 Tesla--feasibility study and preliminary results using optimized venous saturation pulses
- PMID: 25232868
- PMCID: PMC4169393
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106697
Improved cerebral time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography at 7 Tesla--feasibility study and preliminary results using optimized venous saturation pulses
Abstract
Purpose: Conventional saturation pulses cannot be used for 7 Tesla ultra-high-resolution time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF MRA) due to specific absorption rate (SAR) limitations. We overcome these limitations by utilizing low flip angle, variable rate selective excitation (VERSE) algorithm saturation pulses.
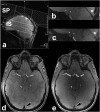
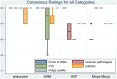
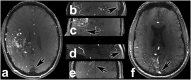
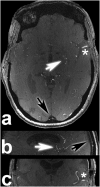
Material and methods: Twenty-five neurosurgical patients (male n = 8, female n = 17; average age 49.64 years; range 26-70 years) with different intracranial vascular pathologies were enrolled in this trial. All patients were examined with a 7 Tesla (Magnetom 7 T, Siemens) whole body scanner system utilizing a dedicated 32-channel head coil. For venous saturation pulses a 35° flip angle was applied. Two neuroradiologists evaluated the delineation of arterial vessels in the Circle of Willis, delineation of vascular pathologies, presence of artifacts, vessel-tissue contrast and overall image quality of TOF MRA scans in consensus on a five-point scale. Normalized signal intensities in the confluence of venous sinuses, M1 segment of left middle cerebral artery and adjacent gray matter were measured and vessel-tissue contrasts were calculated.
Results: Ratings for the majority of patients ranged between good and excellent for most of the evaluated features. Venous saturation was sufficient for all cases with minor artifacts in arteriovenous malformations and arteriovenous fistulas. Quantitative signal intensity measurements showed high vessel-tissue contrast for confluence of venous sinuses, M1 segment of left middle cerebral artery and adjacent gray matter.
Conclusion: The use of novel low flip angle VERSE algorithm pulses for saturation of venous vessels can overcome SAR limitations in 7 Tesla ultra-high-resolution TOF MRA. Our protocol is suitable for clinical application with excellent image quality for delineation of various intracranial vascular pathologies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
High resolution, magnetization transfer saturation, variable flip angle, time-of-flight MRA in the detection of intracranial vascular stenoses.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1995 Sep-Oct;19(5):700-6. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199509000-00003. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1995. PMID: 7560313
-
Time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography at 7 T using venous saturation pulses with reduced flip angles.Invest Radiol. 2012 Aug;47(8):445-50. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e31824ef21f. Invest Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22766907
-
Contrast enhancement in TOF cerebral angiography at 7 T using saturation and MT pulses under SAR constraints: impact of VERSE and sparse pulses.Magn Reson Med. 2012 Jul;68(1):188-97. doi: 10.1002/mrm.23226. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Magn Reson Med. 2012. PMID: 22139829 Free PMC article.
-
[Intracranial MR angiography].Radiologe. 1994 Aug;34(8):437-46. Radiologe. 1994. PMID: 7972721 Review. German.
-
Neurovascular imaging at 1.5 tesla versus 3.0 tesla.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2009 Feb;17(1):29-46. doi: 10.1016/j.mric.2008.12.005. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2009. PMID: 19364598 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of superficial temporal artery-middle cerebral artery double bypass in patients with hemorrhagic moyamoya disease: surgical effects for operated hemispheric sides.Neurosurg Rev. 2019 Jun;42(2):559-568. doi: 10.1007/s10143-018-01059-z. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Neurosurg Rev. 2019. PMID: 30511308
-
Highest Resolution In Vivo Human Brain MRI Using Prospective Motion Correction.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 30;10(7):e0133921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133921. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26226146 Free PMC article.
-
Improved visualization of superficial temporal artery using segmented time-of-flight MR angiography with venous suppression at 7T.Neuroradiology. 2018 Nov;60(11):1243-1246. doi: 10.1007/s00234-018-2099-9. Epub 2018 Sep 22. Neuroradiology. 2018. PMID: 30244414
-
Perspectives of Ultra-High-Field MRI in Neuroradiology.Clin Neuroradiol. 2015 Oct;25 Suppl 2:267-73. doi: 10.1007/s00062-015-0437-4. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Clin Neuroradiol. 2015. PMID: 26184503 Review.
-
Giant Intracranial Aneurysms at 7T MRI.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016 Apr;37(4):636-41. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4569. Epub 2015 Nov 12. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016. PMID: 26564437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keller PJ, Drayer BP, Fram EK, Williams KD, Dumoulin CL, et al. (1989) MR angiography with two-dimensional acquisition and three-dimensional display. Work in progress. Radiology 173: 527–532. - PubMed
-
- Brugieres P, Ricolfi F, Revel MP, Combes C, Gaston A (1993) Functional exploration of brain vessels by MRI. Usefulness of presaturation techniques. Journal of Neuroradiology 20: 239–251. - PubMed
-
- Brugières P, Blustajn J, Le Guérinel C, Méder JF, Thomas P, et al. (1998) Magnetic resonance angiography of giant intracranial aneurysms. Neuroradiology 40: 96–102. - PubMed
-
- Monninghoff C, Maderwald S, Theysohn JM, Kraff O, Ladd SC, et al. (2009) Evaluation of intracranial aneurysms with 7 T versus 1.5 T time-of-flight MR angiography - initial experience. RoFo: Fortschritte auf dem Gebiete der Rontgenstrahlen und der Nuklearmedizin 181: 16–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

