Discovery of a small molecule that inhibits bacterial ribosome biogenesis
- PMID: 25233066
- PMCID: PMC4371806
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03574
Discovery of a small molecule that inhibits bacterial ribosome biogenesis
Abstract
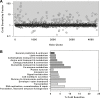
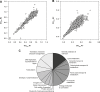
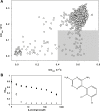
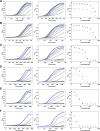
While small molecule inhibitors of the bacterial ribosome have been instrumental in understanding protein translation, no such probes exist to study ribosome biogenesis. We screened a diverse chemical collection that included previously approved drugs for compounds that induced cold sensitive growth inhibition in the model bacterium Escherichia coli. Among the most cold sensitive was lamotrigine, an anticonvulsant drug. Lamotrigine treatment resulted in the rapid accumulation of immature 30S and 50S ribosomal subunits at 15 °C. Importantly, this was not the result of translation inhibition, as lamotrigine was incapable of perturbing protein synthesis in vivo or in vitro. Spontaneous suppressor mutations blocking lamotrigine activity mapped solely to the poorly characterized domain II of translation initiation factor IF2 and prevented the binding of lamotrigine to IF2 in vitro. This work establishes lamotrigine as a widely available chemical probe of bacterial ribosome biogenesis and suggests a role for E. coli IF2 in ribosome assembly.
Keywords: E. coli; biochemistry; cold sensitivity; infectious disease; lamotrigine; microbiology; ribosome biogenesis; translation initiation factor IF2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures

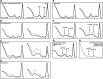
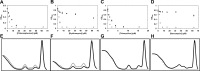
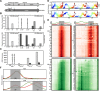
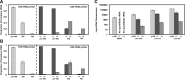


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

