Aquaporin-3 re-expression induces differentiation in a phospholipase D2-dependent manner in aquaporin-3-knockout mouse keratinocytes
- PMID: 25233074
- PMCID: PMC7278525
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2014.412
Aquaporin-3 re-expression induces differentiation in a phospholipase D2-dependent manner in aquaporin-3-knockout mouse keratinocytes
Abstract
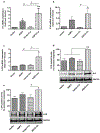
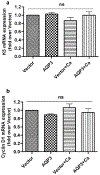
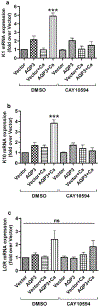
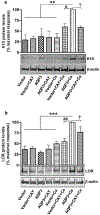
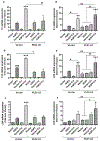
Aquaporin-3 (AQP3) is a water and glycerol channel expressed in epidermal keratinocytes. Despite many studies, controversy remains about the role of AQP3 in keratinocyte differentiation. Previously, our laboratory has shown co-localization of AQP3 and phospholipase D2 (PLD2) in caveolin-rich membrane microdomains. We hypothesized that AQP3 transports glycerol and "funnels" this primary alcohol to PLD2 to form a pro-differentiative signal, such that the action of AQP3 to induce differentiation should require PLD2. To test this idea, we re-expressed AQP3 in mouse keratinocytes derived from AQP3-knockout mice. The re-expression of AQP3, which increased [3H]glycerol uptake, also induced mRNA and protein expression of epidermal differentiation markers such as keratin 1, keratin 10, and loricrin, with or without the induction of differentiation by an elevated extracellular calcium concentration. Re-expression of AQP3 had no effect on the expression of the proliferation markers keratin 5 and cyclin D1. Furthermore, a selective inhibitor of PLD2, CAY10594, and a lipase-dead (LD) PLD2 mutant, but not a LD PLD1 mutant, significantly inhibited AQP3 re-expression-induced differentiation marker expression with calcium elevation, suggesting a role for PLD2 in this process. Thus, our results indicate that AQP3 has a pro-differentiative role in epidermal keratinocytes and that PLD2 activity is necessary for this effect.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
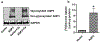
Similar articles
-
A potential role for the phospholipase D2-aquaporin-3 signaling module in early keratinocyte differentiation: production of a phosphatidylglycerol signaling lipid.J Invest Dermatol. 2007 Dec;127(12):2823-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700921. Epub 2007 Jun 28. J Invest Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17597824
-
Aquaporin-3 in keratinocytes and skin: its role and interaction with phospholipase D2.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2011 Apr 15;508(2):138-43. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2011.01.014. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2011. PMID: 21276418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide decreases phosphatidylglycerol levels and inhibits calcium-induced differentiation in mouse keratinocytes.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 13;8(11):e80946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080946. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24236206 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of differentiation markers in aquaporin-3 deficient epidermis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2009 Mar;301(3):245-52. doi: 10.1007/s00403-009-0927-9. Epub 2009 Jan 31. Arch Dermatol Res. 2009. PMID: 19184071 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of aquaporin-3 in the epidermis.J Invest Dermatol. 2008 Sep;128(9):2145-51. doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.70. Epub 2008 Jun 12. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18548108 Review.
Cited by
-
Cannabidiol Application Increases Cutaneous Aquaporin-3 and Exerts a Skin Moisturizing Effect.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Aug 30;14(9):879. doi: 10.3390/ph14090879. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34577578 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of PGC-1α in Aging Skin Barrier Function.Cells. 2024 Jul 2;13(13):1135. doi: 10.3390/cells13131135. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38994987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabidiol-Mediated Changes to the Phospholipid Profile of UVB-Irradiated Keratinocytes from Psoriatic Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 9;21(18):6592. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186592. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32916896 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylglycerol Inhibits Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated Inflammation by Danger-Associated Molecular Patterns.J Invest Dermatol. 2019 Apr;139(4):868-877. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.10.021. Epub 2018 Oct 31. J Invest Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30391260 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporins in Skin.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1398:211-223. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-7415-1_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 36717497
References
-
- Banno Y (2002) Regulation and possible role of mammalian phospholipase D in cellular functions. J Biochem 131:301–306. - PubMed
-
- Bellemere G, Von Stetten O, Oddos T (2008) Retinoic acid increases aquaporin 3 expression in normal human skin. J Invest Dermatol 128:542–548. - PubMed
-
- Bikle DD, Pillai S (1993) Vitamin D, calcium, and epidermal differentiation. Endocr Rev 14:3–19. - PubMed
-
- Bollag WB, Xie D, Zheng X, et al. (2007) A potential role for the phospholipase D2-aquaporin-3 signaling module in early keratinocyte differentiation: production of a phosphatidylglycerol signaling lipid. J Invest Dermatol 127:2823–2831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

