Visual dependency and dizziness after vestibular neuritis
- PMID: 25233234
- PMCID: PMC4169430
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105426
Visual dependency and dizziness after vestibular neuritis
Abstract
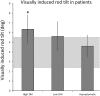
Symptomatic recovery after acute vestibular neuritis (VN) is variable, with around 50% of patients reporting long term vestibular symptoms; hence, it is essential to identify factors related to poor clinical outcome. Here we investigated whether excessive reliance on visual input for spatial orientation (visual dependence) was associated with long term vestibular symptoms following acute VN. Twenty-eight patients with VN and 25 normal control subjects were included. Patients were enrolled at least 6 months after acute illness. Recovery status was not a criterion for study entry, allowing recruitment of patients with a full range of persistent symptoms. We measured visual dependence with a laptop-based Rod-and-Disk Test and severity of symptoms with the Dizziness Handicap Inventory (DHI). The third of patients showing the worst clinical outcomes (mean DHI score 36-80) had significantly greater visual dependence than normal subjects (6.35° error vs. 3.39° respectively, p = 0.03). Asymptomatic patients and those with minor residual symptoms did not differ from controls. Visual dependence was associated with high levels of persistent vestibular symptoms after acute VN. Over-reliance on visual information for spatial orientation is one characteristic of poorly recovered vestibular neuritis patients. The finding may be clinically useful given that visual dependence may be modified through rehabilitation desensitization techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Cutfield NJ, Seemungal BM, Millington H, Bronstein AM (2011) Diagnosis of acute vertigo in the emergency department. EmergMedJ 28: 538–539. - PubMed
-
- Schuknecht HF, Kitamura K (1981) Second Louis H. Clerf Lecture. Vestibular neuritis. The Annals of otology, rhinology & laryngologySupplement 90: 1–19. - PubMed
-
- Curthoys IS, Halmagyi GM (1995) Vestibular compensation: a review of the oculomotor, neural, and clinical consequences of unilateral vestibular loss. JVestibRes 5: 67–107. - PubMed
-
- Imate Y, Sekitani T (1993) Vestibular compensation in vestibular neuronitis. Long-term follow-up evaluation. Acta Otolaryngol 113: 463–465. - PubMed
-
- Bergenius J, Perols O (1999) Vestibular neuritis: a follow-up study. Acta Otolaryngol 119: 895–899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

