Ribosome rescue and translation termination at non-standard stop codons by ICT1 in mammalian mitochondria
- PMID: 25233460
- PMCID: PMC4169044
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004616
Ribosome rescue and translation termination at non-standard stop codons by ICT1 in mammalian mitochondria
Abstract
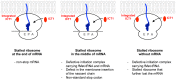
Release factors (RFs) govern the termination phase of protein synthesis. Human mitochondria harbor four different members of the class 1 RF family: RF1Lmt/mtRF1a, RF1mt, C12orf65 and ICT1. The homolog of the essential ICT1 factor is widely distributed in bacteria and organelles and has the peculiar feature in human mitochondria to be part of the ribosome as a ribosomal protein of the large subunit. The factor has been suggested to rescue stalled ribosomes in a codon-independent manner. The mechanism of action of this factor was obscure and is addressed here. Using a homologous mitochondria system of purified components, we demonstrate that the integrated ICT1 has no rescue activity. Rather, purified ICT1 binds stoichiometrically to mitochondrial ribosomes in addition to the integrated copy and functions as a general rescue factor, i.e. it releases the polypeptide from the peptidyl tRNA from ribosomes stalled at the end or in the middle of an mRNA or even from non-programmed ribosomes. The data suggest that the unusual termination at a sense codon (AGA/G) of the oxidative-phosphorylation enzymes CO1 and ND6 is also performed by ICT1 challenging a previous model, according to which RF1Lmt/mtRF1a is responsible for the translation termination at non-standard stop codons. We also demonstrate by mutational analyses that the unique insertion sequence present in the N-terminal domain of ICT1 is essential for peptide release rather than for ribosome binding. The function of RF1mt, another member of the class1 RFs in mammalian mitochondria, was also examined and is discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Comment in
-
Response to the Formal Letter of Z. Chrzanowska-Lightowlers and R. N. Lightowlers Regarding Our Article "Ribosome Rescue and Translation Termination at Non-Standard Stop Codons by ICT1 in Mammalian Mitochondria".PLoS Genet. 2015 Jun 18;11(6):e1005218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005218. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26087150 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to "Ribosome Rescue and Translation Termination at Non-standard Stop Codons by ICT1 in Mammalian Mitochondria".PLoS Genet. 2015 Jun 18;11(6):e1005227. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005227. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26087262 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Response to the Formal Letter of Z. Chrzanowska-Lightowlers and R. N. Lightowlers Regarding Our Article "Ribosome Rescue and Translation Termination at Non-Standard Stop Codons by ICT1 in Mammalian Mitochondria".PLoS Genet. 2015 Jun 18;11(6):e1005218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005218. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26087150 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Structural basis of translation termination, rescue, and recycling in mammalian mitochondria.Mol Cell. 2021 Jun 17;81(12):2566-2582.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.03.042. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33878294
-
Response to "Ribosome Rescue and Translation Termination at Non-standard Stop Codons by ICT1 in Mammalian Mitochondria".PLoS Genet. 2015 Jun 18;11(6):e1005227. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005227. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26087262 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Diversity and Similarity of Termination and Ribosome Rescue in Bacterial, Mitochondrial, and Cytoplasmic Translation.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2021 Sep;86(9):1107-1121. doi: 10.1134/S0006297921090066. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2021. PMID: 34565314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual functions of ribosome recycling factor in protein biosynthesis: disassembling the termination complex and preventing translational errors.Biochimie. 1996;78(11-12):959-69. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(97)86718-1. Biochimie. 1996. PMID: 9150873 Review.
Cited by
-
Organization and expression of the mammalian mitochondrial genome.Nat Rev Genet. 2022 Oct;23(10):606-623. doi: 10.1038/s41576-022-00480-x. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Nat Rev Genet. 2022. PMID: 35459860 Review.
-
Dealing with an Unconventional Genetic Code in Mitochondria: The Biogenesis and Pathogenic Defects of the 5-Formylcytosine Modification in Mitochondrial tRNAMet.Biomolecules. 2017 Mar 2;7(1):24. doi: 10.3390/biom7010024. Biomolecules. 2017. PMID: 28257121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial transcription and translation: overview.Essays Biochem. 2018 Jul 20;62(3):309-320. doi: 10.1042/EBC20170102. Print 2018 Jul 20. Essays Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30030363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A stalled-ribosome rescue factor Pth3 is required for mitochondrial translation against antibiotics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Commun Biol. 2021 Mar 8;4(1):300. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01835-6. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33686140 Free PMC article.
-
Response to the Formal Letter of Z. Chrzanowska-Lightowlers and R. N. Lightowlers Regarding Our Article "Ribosome Rescue and Translation Termination at Non-Standard Stop Codons by ICT1 in Mammalian Mitochondria".PLoS Genet. 2015 Jun 18;11(6):e1005218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005218. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26087150 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

