The role of airway epithelial cells and innate immune cells in chronic respiratory disease
- PMID: 25234144
- PMCID: PMC4782595
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3739
The role of airway epithelial cells and innate immune cells in chronic respiratory disease
Abstract
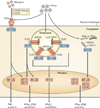
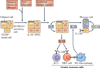
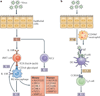
An abnormal immune response to environmental agents is generally thought to be responsible for causing chronic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Based on studies of experimental models and human subjects, there is increasing evidence that the response of the innate immune system is crucial for the development of this type of airway disease. Airway epithelial cells and innate immune cells represent key components of the pathogenesis of chronic airway disease and are emerging targets for new therapies. In this Review, we summarize the innate immune mechanisms by which airway epithelial cells and innate immune cells regulate the development of chronic respiratory diseases. We also explain how these pathways are being targeted in the clinic to treat patients with these diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Minino AM, Murphy SL, Xu J, Kochanek KD. National vital statistics reports. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2011. - PubMed
-
- Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, editors. World Health Organization. Global surveillance, prevention and control of chronic respiratory diseases: a comprehensive approach. WHO; 2007.
-
- Spits H, Cupedo T. Innate lymphoid cells: emerging insights in development, lineage relationships, and function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012;30:647–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P01 HL029594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 HL123429/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50-HL107183/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121791/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL121168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL107183/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL29594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI095776/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL121791/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19-AI070489/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI095776/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI070489/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI111605/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

