Changes in the built environment and changes in the amount of walking over time: longitudinal results from the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 25234431
- PMCID: PMC4188343
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwu218
Changes in the built environment and changes in the amount of walking over time: longitudinal results from the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis
Abstract
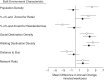
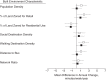
Lack of longitudinal research hinders causal inference on the association between the built environment and walking. In the present study, we used data from 6,027 adults in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis who were 45-84 years of age at baseline to investigate the association of neighborhood built environment with trends in the amount of walking between 2000 and 2012. Walking for transportation and walking for leisure were assessed at baseline and at 3 follow-up visits (median follow-up = 9.15 years). Time-varying built environment measures (measures of population density, land use, number of destinations, bus access, and street connectivity) were created using geographic information systems. We used linear mixed models to estimate the associations between baseline levels of and a change in each built environment feature and a change in the frequency of walking. After adjustment for potential confounders, we found that higher baseline levels of population density, area zoned for retail, social destinations, walking destinations, and street connectivity were associated with greater increases in walking for transportation over time. Higher baseline levels of land zoned for residential use and distance to buses were associated with less pronounced increases (or decreases) in walking for transportation over time. Increases in the number of social destinations, the number of walking destinations, and street connectivity over time were associated with greater increases in walking for transportation. Higher baseline levels of both land zoned for retail and walking destinations were associated with greater increases in leisure walking, but no changes in built environment features were associated with leisure walking. The creation of mixed-use, dense developments may encourage adults to incorporate walking for transportation into their everyday lives.
Keywords: environment design; geographic information systems; leisure activities; longitudinal/prospective studies; neighborhoods; residence characteristics; transportation; walking.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Kohl HW. Physical activity and cardiovascular disease: evidence for a dose response. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001;33(6 suppl):S472–S483. - PubMed
-
- Zhao G, Ford ES, Li C, et al. Physical activity in U.S. older adults with diabetes mellitus: prevalence and correlates of meeting physical activity recommendations. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(1):132–137. - PubMed
-
- Eyre H, Kahn R, Robertson RM, et al. Preventing cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes: a common agenda for the American Cancer Society, the American Diabetes Association, and the American Heart Association. CA Cancer J Clin. 2004;54(4):190–207. - PubMed
-
- Sallis JF, Owen N, Fisher EB. Ecological models of health behavior. In: Glanz K, Rimer BK, Viswanath K, editors. Health Behavior and Health Education: Theory, Research, and Practice. 4th ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass by John Wiley & Sons; 2008. pp. 465–486.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01 HL071759/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-TR-000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007168/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071759/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-TR-001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

