Neural correlates of strategic reasoning during competitive games
- PMID: 25236468
- PMCID: PMC4201877
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1256254
Neural correlates of strategic reasoning during competitive games
Abstract
Although human and animal behaviors are largely shaped by reinforcement and punishment, choices in social settings are also influenced by information about the knowledge and experience of other decision-makers. During competitive games, monkeys increased their payoffs by systematically deviating from a simple heuristic learning algorithm and thereby countering the predictable exploitation by their computer opponent. Neurons in the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC) signaled the animal's recent choice and reward history that reflected the computer's exploitative strategy. The strength of switching signals in the dmPFC also correlated with the animal's tendency to deviate from the heuristic learning algorithm. Therefore, the dmPFC might provide control signals for overriding simple heuristic learning algorithms based on the inferred strategies of the opponent.
Copyright © 2014, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
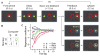
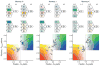
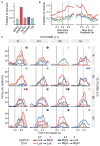
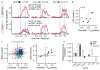
References
-
- Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J. The Elements of Statistical Learning. Springer; New York: 2001.
-
- Gigerenzer G, Brighton H. Homo heuristicus: why biased minds make better inferences. Top Cogn Sci. 2009;1:107–143. - PubMed
-
- Sutton RS, Barto AG. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. MIT Press; Cambridge, MA: 1998.
-
- Ito M, Doya K. Multiple representations and algorithms for reinforcement learning in the cortico-basal ganglia circuit. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2011;21:368–373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

