Quantitative trait locus mapping methods for diversity outbred mice
- PMID: 25237114
- PMCID: PMC4169154
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.114.013748
Quantitative trait locus mapping methods for diversity outbred mice
Abstract
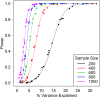
Genetic mapping studies in the mouse and other model organisms are used to search for genes underlying complex phenotypes. Traditional genetic mapping studies that employ single-generation crosses have poor mapping resolution and limit discovery to loci that are polymorphic between the two parental strains. Multiparent outbreeding populations address these shortcomings by increasing the density of recombination events and introducing allelic variants from multiple founder strains. However, multiparent crosses present new analytical challenges and require specialized software to take full advantage of these benefits. Each animal in an outbreeding population is genetically unique and must be genotyped using a high-density marker set; regression models for mapping must accommodate multiple founder alleles, and complex breeding designs give rise to polygenic covariance among related animals that must be accounted for in mapping analysis. The Diversity Outbred (DO) mice combine the genetic diversity of eight founder strains in a multigenerational breeding design that has been maintained for >16 generations. The large population size and randomized mating ensure the long-term genetic stability of this population. We present a complete analytical pipeline for genetic mapping in DO mice, including algorithms for probabilistic reconstruction of founder haplotypes from genotyping array intensity data, and mapping methods that accommodate multiple founder haplotypes and account for relatedness among animals. Power analysis suggests that studies with as few as 200 DO mice can detect loci with large effects, but loci that account for <5% of trait variance may require a sample size of up to 1000 animals. The methods described here are implemented in the freely available R package DOQTL.
Keywords: MPP; Multiparent Advanced Generation Inter-Cross (MAGIC); Multiparental populations; diversity outbred; haplotype reconstruction; quantitative trait locus mapping.
Copyright © 2014 Gatti et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cleaning Genotype Data from Diversity Outbred Mice.G3 (Bethesda). 2019 May 7;9(5):1571-1579. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400165. G3 (Bethesda). 2019. PMID: 30877082 Free PMC article.
-
A generic hidden Markov model for multiparent populations.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Feb 4;12(2):jkab396. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab396. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 34791211 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution genetic mapping in the diversity outbred mouse population identifies Apobec1 as a candidate gene for atherosclerosis.G3 (Bethesda). 2014 Oct 23;4(12):2353-63. doi: 10.1534/g3.114.014704. G3 (Bethesda). 2014. PMID: 25344410 Free PMC article.
-
QTL mapping in outbred populations: successes and challenges.Physiol Genomics. 2014 Feb 1;46(3):81-90. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00127.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Physiol Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24326347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for mapping and cloning quantitative trait genes in rodents.Nat Rev Genet. 2005 Apr;6(4):271-86. doi: 10.1038/nrg1576. Nat Rev Genet. 2005. PMID: 15803197 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell morphology QTL reveal gene by environment interactions in a genetically diverse cell population.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 18:2023.11.18.567597. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.18.567597. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 38014303 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Genetics of aging bone.Mamm Genome. 2016 Aug;27(7-8):367-80. doi: 10.1007/s00335-016-9650-y. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Mamm Genome. 2016. PMID: 27272104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Giving the Genes a Shuffle: Using Natural Variation to Understand Host Genetic Contributions to Viral Infections.Trends Genet. 2018 Oct;34(10):777-789. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.07.005. Epub 2018 Aug 18. Trends Genet. 2018. PMID: 30131185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic mapping in outbred mice reveals overlap in genetic susceptibility for HZE ion- and γ-ray-induced tumors.Sci Adv. 2020 Apr 15;6(16):eaax5940. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax5940. eCollection 2020 Apr. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32494593 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous Stock Populations for Analysis of Complex Traits.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1488:31-44. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6427-7_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27933519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baum L. E., Petrie, T. , Soules, G. , and Weiss, N., 1970. A maximization technique occuring in the statistical analysis of probabilistic functions of Markov chains. Ann. Math. Stat. 41: 164–171
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG038070/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK076050/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 DK087346/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM070683/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1DK087346/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076050/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK056350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM074244/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM076468/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM070683/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
