Modeling of outpatient prescribing process in iran: a gateway toward electronic prescribing system
- PMID: 25237369
- PMCID: PMC4157049
Modeling of outpatient prescribing process in iran: a gateway toward electronic prescribing system
Abstract
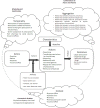
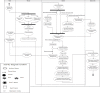
Implementation of electronic prescribing system can overcome many problems of the paper prescribing system, and provide numerous opportunities of more effective and advantageous prescribing. Successful implementation of such a system requires complete and deep understanding of work content, human force, and workflow of paper prescribing. The current study was designed in order to model the current business process of outpatient prescribing in Iran and clarify different actions during this process. In order to describe the prescribing process and the system features in Iran, the methodology of business process modeling and analysis was used in the present study. The results of the process documentation were analyzed using a conceptual model of workflow elements and the technique of modeling "As-Is" business processes. Analysis of the current (as-is) prescribing process demonstrated that Iran stood at the first levels of sophistication in graduated levels of electronic prescribing, namely electronic prescription reference, and that there were problematic areas including bottlenecks, redundant and duplicated work, concentration of decision nodes, and communicative weaknesses among stakeholders of the process. Using information technology in some activities of medication prescription in Iran has not eliminated the dependence of the stakeholders on paper-based documents and prescriptions. Therefore, it is necessary to implement proper system programming in order to support change management and solve the problems in the existing prescribing process. To this end, a suitable basis should be provided for reorganization and improvement of the prescribing process for the future electronic systems.
Keywords: Electronic prescribing; Medication prescription; Model; Process analysis; Workflow.
Figures
References
-
- Hypponen H, Salmivalli L, Sumi R. Organazing for a national infrastructure project: the case of the Finnish electronic prescription. 38th Hawaii International Conference on System Science; Hilton Waikoloa Village, Big Island, Hawaii. IEEE; 2005.
-
- Adang E, Voordijk L, Jan van der Wilt G, Ament A. Cost-effectiveness analysis in relation to budgetary constraints and reallocative restrictions. Health Policy . 2005;74:146–56. - PubMed
-
- Phillips DP, Christenfeld N, Glynn LM. Increase in US medication-error deaths. Lancet. 1998;351:643–644. - PubMed
-
- Kohn LT, Corrigan J, Donaldson MS. Washington DC: national Academies Press; 2000. [[cited 2012 Oct 15]]. To err is human: building a safer health system. Available from:URL: http://www.providersedge.com/ehdocs/ehr_articles/to_err_is_human_%20buil.... - PubMed
-
- Mosleh A, Darbooy SH, Khoshnevis Ansari SH, Mohammadi M. Drug prescription based on WHO indicators: Tehran university of medical sciences facilities with pharmacy. Tehran Uni. Med. J. 2007;65:12–15.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials